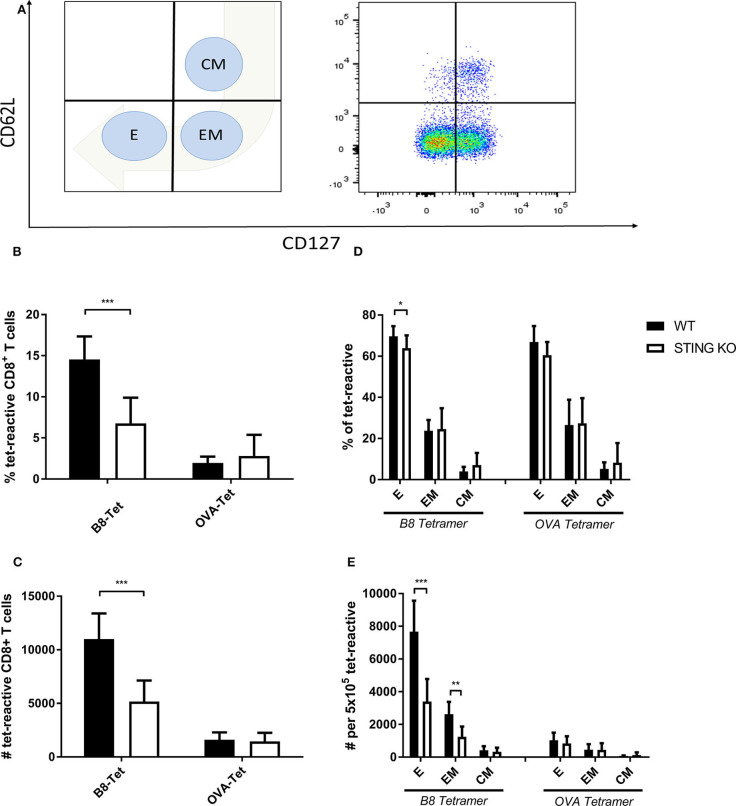
Figure 2.
Maturation and differentiation of B8-specific immunodominant CD8+ T cells is STING-dependent. STING KO mice (STING KO) and WT-littermates (WT) were vaccinated on day 0 i. p. with 107 IU MVA-P7.5-OVA. Seven days after the prime antigen-specific CD8+ T cells were analyzed ex vivo by flow cytometry for their memory phenotype by expression of CD62L and CD127. (A) Presentation of the gating strategy and division into the individual memory subtypes. Analysis of the (B) relative frequency (%) and (C) absolute numbers of B8- or OVA-specific CD8+ T cell responses determined by tetramer staining (tet-reactive). In addition, the respective memory T cell subpopulations [effector T cells (E), effector memory T cells (EM) and central memory T cells (CM)] within the tetramer-reactive fraction are shown in (D) frequencies and (E) absolute numbers. B8 tetramer: n = 13; OVA tetramer: n = 11. Data are represented as mean ± SD of n = 13 (for B8 tetramer) or n = 11 (for OVA tetramer) mice per group pooled from three independent experiments for B. Statistical significance (P); *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001.