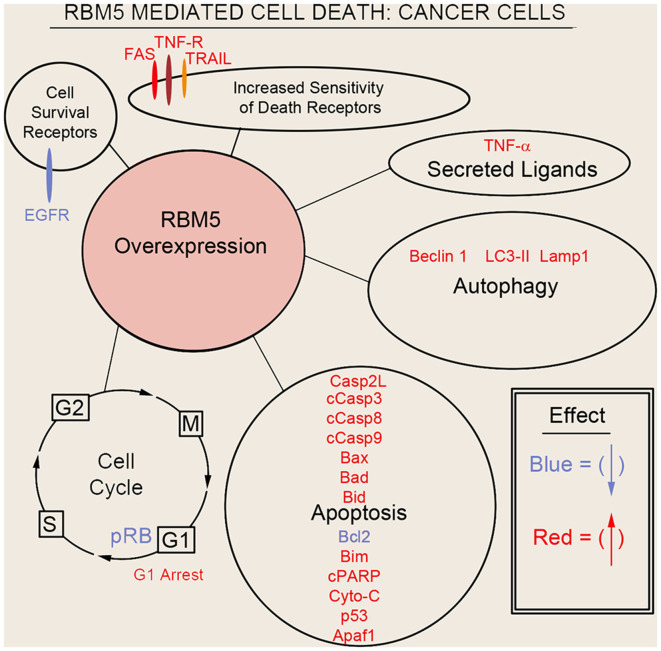
Figure 3.
Mechanisms of RBM5-mediated cell death in cancer. The major signaling mechanisms mediating RBM5 pro-death activity are illustrated. Different processes are separated by circles/ovals. Most of the evidence comes from studies in which RBM5 was overexpressed. Targets in red indicate that their levels were increased with RBM5 overexpression. Targets in blue indicate their levels were decreased with RBM5 overexpression. All studies supporting the depictions in the diagram are cited in the main text. Apoptosis antigen 1 (APO-1/FAS), Tumor necrosis factor receptor (TNF-R), TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL), Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), Microtubule-associated protein 1A/1B-light chain 3 II (LC3-II), Lysosomal-associated membrane protein 1 (LAMP1), Caspase-2-long (Casp2L), Cleaved caspase-3 (cCasp3), Cleaved caspase-8 (cCasp8), Cleaved caspase-9 (cCasp9), BCL2 Associated X (BAX), Bcl2 antagonist of cell death (BAD), BH3 Interacting Domain Death Agonist (BID), B-cell CLL/lymphoma 2 (BCL2), Bcl-2-like 11 (Bcl-2L11/BIM), Cleaved poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (cPARP), Cytochrome c (Cyto-C), cellular tumor antigen p53 (p53), Apoptotic protease activating factor 1 (Apaf1), phosphorylated retinoblastoma protein (pRB), G2 Interphase (G2), Mitosis and cytokinesis phase (M), G1 phase (G1), Synthesis phase (S), epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR).