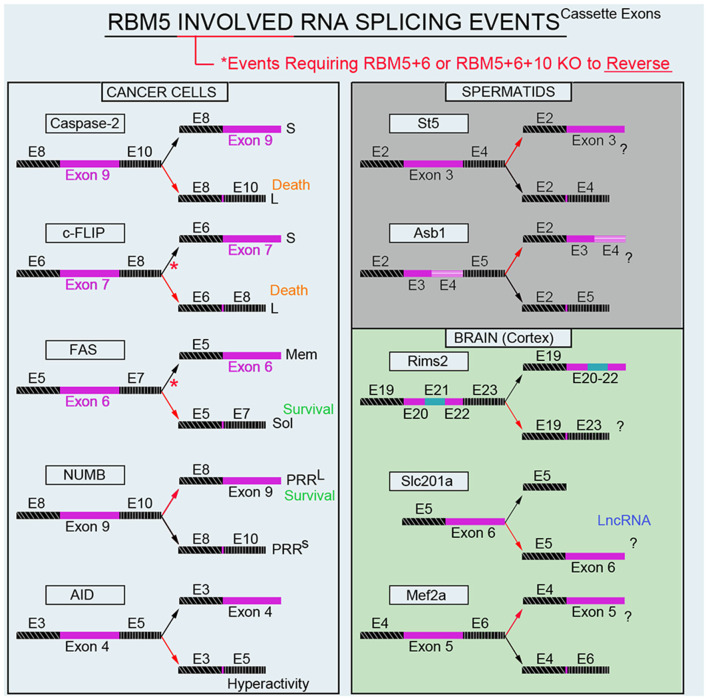
Figure 4.
RBM5-regulated gene-splicing targets in cancer lines, testes, and in cortical brain tissue. Spliced cassette exon(s) are indicated in maroon. Red arrows indicate the direction of splicing that RBM5 favors. Red asterisks indicate that RBM5 and one or more of its paralogues (RBM6 or RBM10) had to be simultaneously inhibited to shift the gene-splicing event in the opposite direction. All studies relevant to the depictions in the diagram are cited in the main text. Cellular FLICE-like inhibitory protein (c-FLIP), apoptosis antigen 1 (APO-1/FAS), NUMB endocytic adaptor protein (NUMB), Activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID), Suppression of tumorigenicity 5 (St5), Ankyrin repeat and SOCS box containing 1 (Asb1), Regulating synaptic membrane exocytosis 2 (Rims2), phosphate (Pi) transporter slc201a (Slc201a), Myocyte enhancer factor 2A (Mef2a).