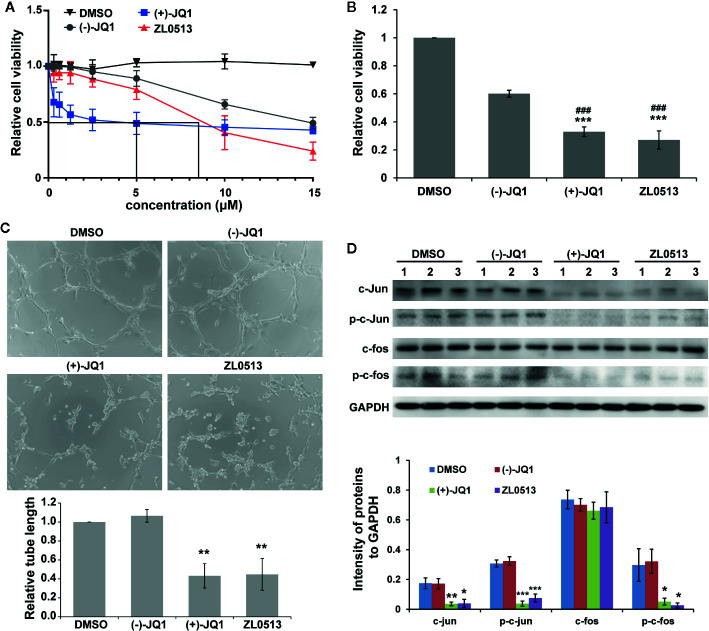
Figure 4.
ZL0513 inhibits the viability and tube formation of HUVECs by inactivating AP-1 expression. (A) Relative cell viability of the HUVECs treated with the indicated concentrations of DMSO (solvent control), (−)-JQ1 (negative control), (+)-JQ1 (1), or ZL0513 (7). (B) Relative viability of the HUVECs was determined using CCK8 assays after 8.5 μM (−)-JQ1, (+)-JQ1 (1), or ZL0513 (7) treatment for 96 h. Both (+)-JQ1 (1) and ZL0513 (7) significantly inhibited cell viability compared with DMSO or (−)-JQ1. (C) Representative HUVEC tube formation after treatment with DMSO, (−)-JQ1, (+)-JQ1 (1), or ZL0513 (7). HUVECs, which were pretreated with DMSO, (−)-JQ1, (+)-JQ1 (1), or ZL0513 (7) for 48 h, were harvested and seeded in Matrigel. Each figure is representative of at least three independent repeats. Statistical analysis of the length of the tube showed that (+)-JQ1 (1) and ZL0513 (7), but not (−)-JQ1, significantly inhibited tube length of the HUVECs compared with the effect of DMSO. (D) The expression of AP-1 components in the HUVECs treated with DMSO, (−)-JQ1, (+)-JQ1 (1), or ZL0513 (7). The expression of total proteins and phosphorylation of c-jun and c-fos were significantly decreased in the HUVECs treated with (+)-JQ1 (1) or ZL0513 (7) at the same dose. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 that compared with the DMSO group; ###P < 0.001 compared with the (−)-JQ1 group. Scale bars: 50 μm.