FIGURE 1.
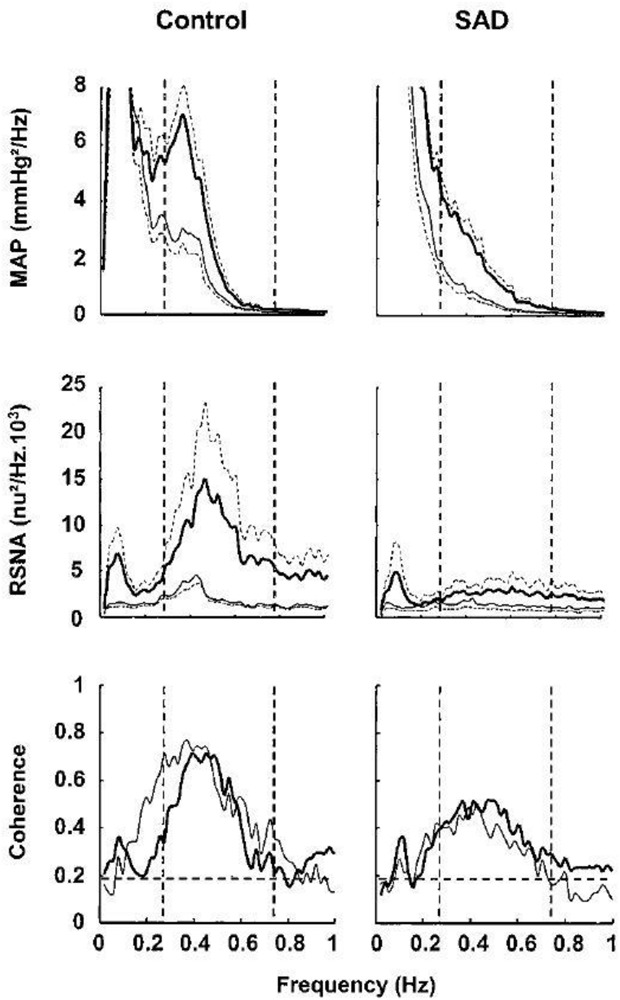
Sinoaortic denervation reduces spectral power of Mayer waves in mean arterial pressure (MAP) and renal sympathetic nerve activity (RSNA) in conscious rats. Central tendency of Mayer waves (low-frequency oscillations) varies across species and approximates 0.4 Hz in rats (range 0.2–0.8 Hz; dashed lines). Recordings of mean arterial pressure and renal sympathetic nerve activity were contemporaneously performed in sham-operated (CONTROL) (n = 10; heavy lines) and sinoaortic-denervated (SAD) (n = 10; thin lines) conscious rats. Fast Fourier transformation (34 periods of 204.8-s duration, representing 2048 data points, overlapping by half the recorded epoch) was employed to determine power spectral density and coherence. Renal sympathetic nerve activity constituent spectral bands were normalized to mean burst power determined in precession to spectral analysis. Hz, hertz (cycles/s); n.u., normalized units. Modified with permission from Figure 1 of Julien (2006).
