Figure 5. YopM binding to and phosphorylation of FMF mutant human pyrin is substantially reduced relative to WT human pyrin.
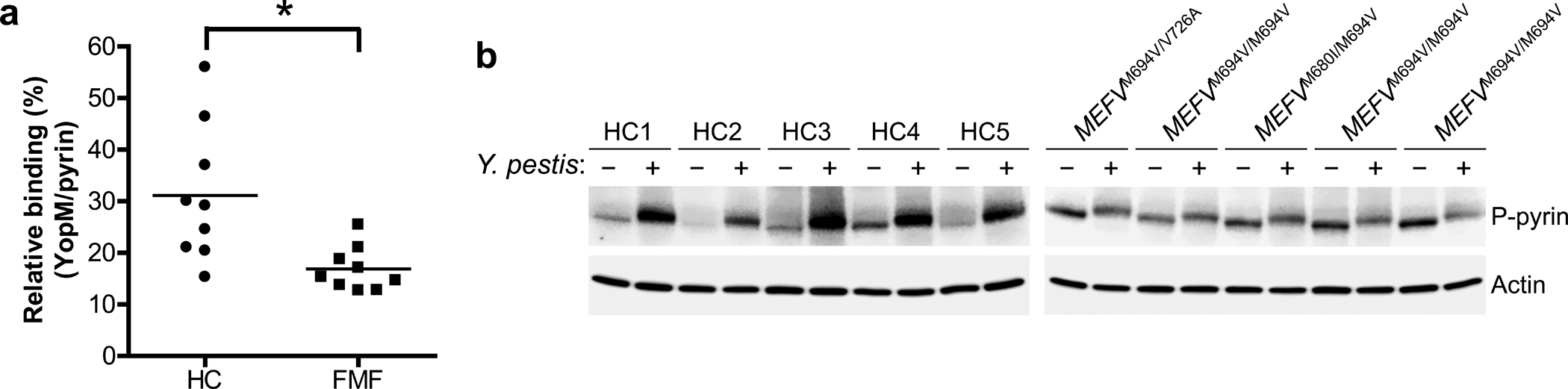
a, YopM-pyrin binding assay with immunoprecipitation from lysates of CD14+ monocytes of PBMCs from healthy controls (n=9) or FMF patients (n=9) with homozygous or compound heterozygous common FMF mutations (MEFV_p.M680I, MEFV_p.M694V, or MEFV_p.V726A) infected with Y. pestis. Proteins immunoprecipitated with antibody to pyrin were analyzed by immunoblotting with an antibody specific to YopM. The densities of YopM or pyrin bands were measured by Fc-Odyssey (Li-cor), and each YopM band in immunoprecipitated proteins was normalized by pyrin band. Each symbol represents an individual person; horizontal lines indicate the mean. *P = 0.0121 (unpaired two-tailed t test). b, Immunoblot analysis of phosphorylated pyrin in lysates of CD14+ monocytes from healthy controls (n=5) or FMF patients (n=5) with indicated mutations infected with Y. pestis, MOI 0 (−) or MOI 30 (+). Shown is an immunoblot from a single biological replicate.
