Extended Data Fig. 4 |. TALE–split DddAtox proteins mediate efficient base editing in nuclear DNA of U2OS cells.
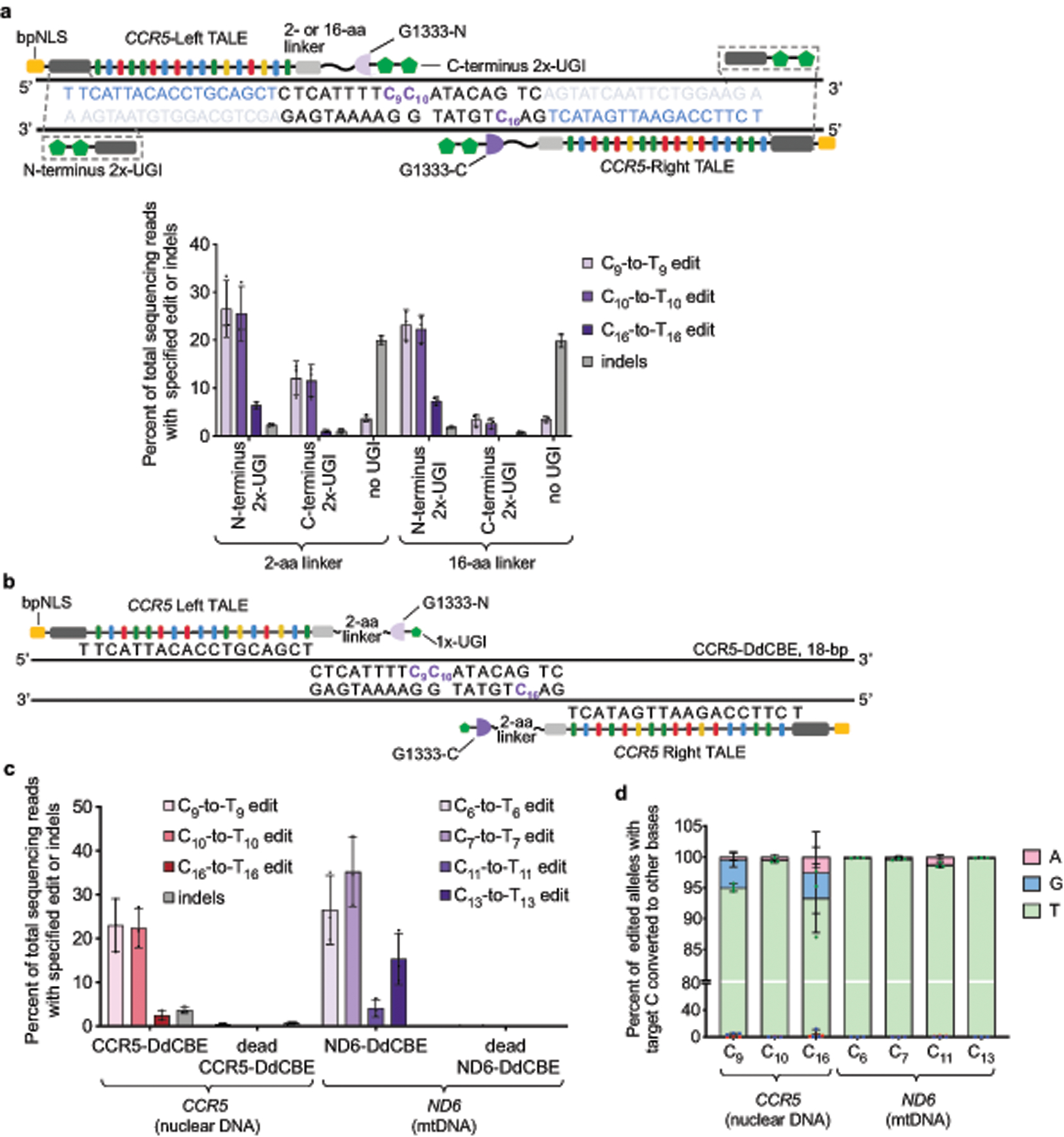
a, Left–G1333-DddAtox-N and Right–G1333-DddAtox-C bind DNA sequences within CCR5. Target cytosines are shown in purple and TALE binding sites are shown in blue. Two copies of UGI proteins (2×-UGI) were fused to the N- or C terminus through a 2- or 16-amino acid linker. Editing efficiencies and indel frequencies for the possible combinations of UGI positions and linker lengths are shown. In the absence of UGI protein, only C9-to-T9 edit was observed. b, Architecture of nuclear-targeting CCR5-DdCBE (see Fig. 3c for optimized DdCBE architecture targeting mtDNA). Target cytosines are shown in purple. c, Editing efficiencies and indel frequencies of cells treated with CCR5-DdCBE and ND6-DdCBE 3-days-post transfection are shown. Dead-DdCBEs containing the inactive DddAtox(E1347A) mutant were used as negative controls. d, Outcomes among edited alleles in which the specified target C is mutated are shown for the indicated base editor. Values and error bars in a, c and d reflect the mean ± s.d. of n = 3 independent biological replicates.
