Figure 4.
RPA-Based COVID-19 Test
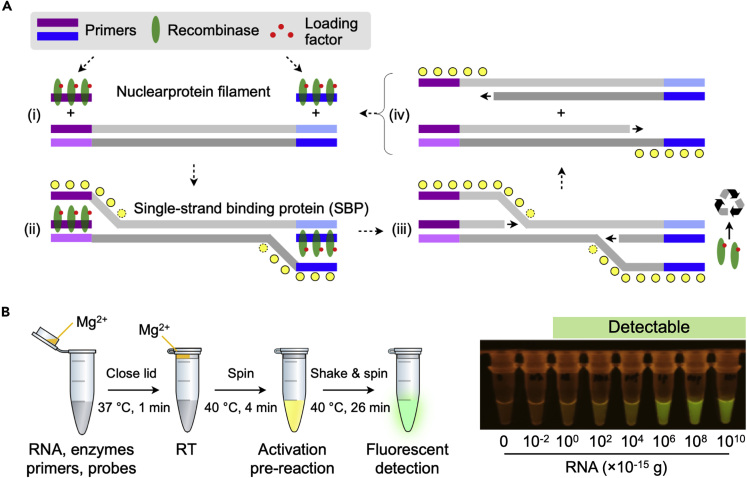
(A) RPA mechanism. RPA reaction mix contains recombinase, primers, loading factors, and single-stranded binding proteins. (i) The recombinase binds to primers in the presence of loading factors, forming nucleoprotein filaments. (ii) This complex binds to complementary sequences in the target DNA, forming D loop structure, and initiates strand exchange. Single-stranded binding proteins stabilize the displaced DNA stands. (iii) Recombinase disassembles from the nucleoprotein filament to be re-used for subsequent amplification cycles. (iv) DNA polymerase extend primers, separating parallel strands to form duplexes. Repeated cycle of this process enables exponential amplification.
(B) RT-RPA assay developed for COVID-19 diagnostics. Extracted RNA sample is mixed with RT-RPA reaction mixture. RPA activator (Mg2+) is loaded inside the lid of the vial. RT is performed at 37°C (1 min), and then the vial is spun to introduce Mg2+ into the reaction mixture. The reaction vial is heated to 40°C (4 min) for initial RPA activation. After shake and spin, the reaction is let to proceed for additional 26 min at 40°C. The reaction product is then detected via green fluorescence excited by blue light.
Reproduced with permission from Ref (Xia and Chen, 2020).