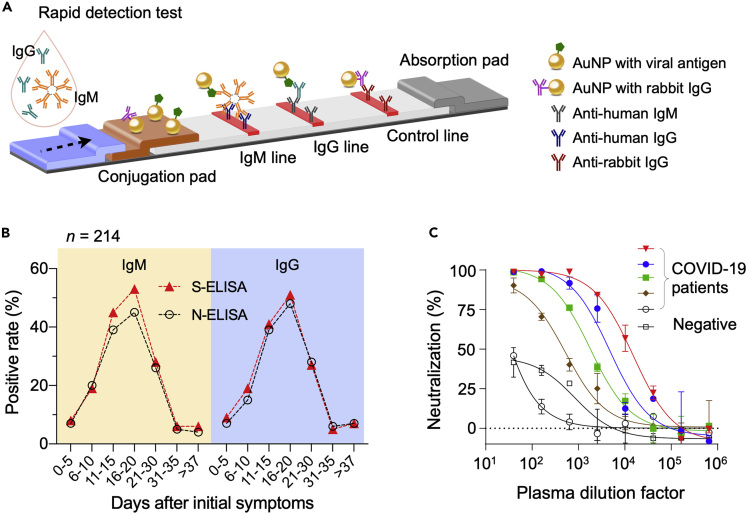
Figure 7.
Examples of COVID-19 Immunoassays
(A) Schematic of a rapid detection test (RDT) device. The sample, dropped on a loading pad, flows through the device via capillary effect and wet colloidal gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) loaded in the conjugation pad. AuNPs tagged with viral antigen bind to IgM and IgG antibodies, and the complexes are captured in the downstream by pre-spotted anti-human IgM and IgG antibodies. AuNP conjugated with non-human IgG antibodies are captured by appropriate antibodies to generate a control signal.
(B) Two types of ELISA were compared. One used recombinant SARS-CoV-2 N protein as a capture antigen (N-ELISA), and the other, recombinant SARS-CoV-2 S protein (S-ELISA). Serum samples from 214 patients with COVID-19 were tested. Overall, S-ELISA showed higher detection rate than N-ELISA.
(C) Plasma samples from patients (n = 5) who recovered from COVID-19 were used for virus neutralization tests. In a concentration-dependent manner, all five plasma inhibited the infection of 293T/ACE2 cells by SARS-CoV-2 pseudo virus. Plasma from a healthy donor was used as a negative control. The median percentage of neutralization is shown from duplicate measurements. Data points represent the median percentage of neutralization. Error bars indicate standard deviation from duplicate measurements.
(B) Adapted with permission from Ref (Liu et al., 2020b). Copyright 2020 American Society for Microbiology. (C) Reproduced with permission from Ref (Wu et al., 2020).