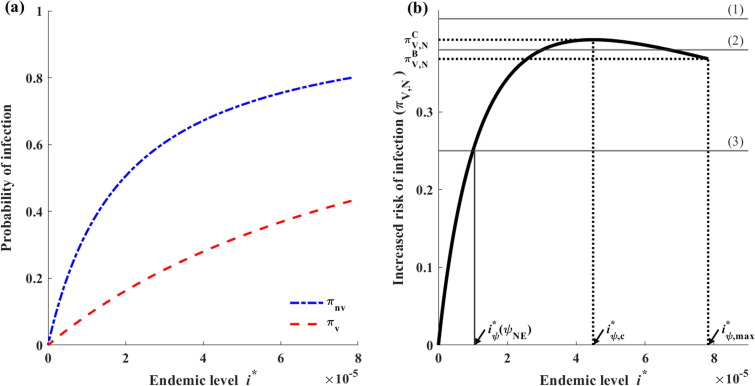
Fig. 6.
Case where (Case 2). Here, we set and . (a) Graph of the probabilities of infection among individuals who accept or reject vaccination. (b) Graph of the differences between two probabilities of infection. If it exists, the Nash vaccination strategy can be obtained when : (1) there is no Nash strategy when , (2) two Nash strategies when , and (3) one Nash strategy when or .