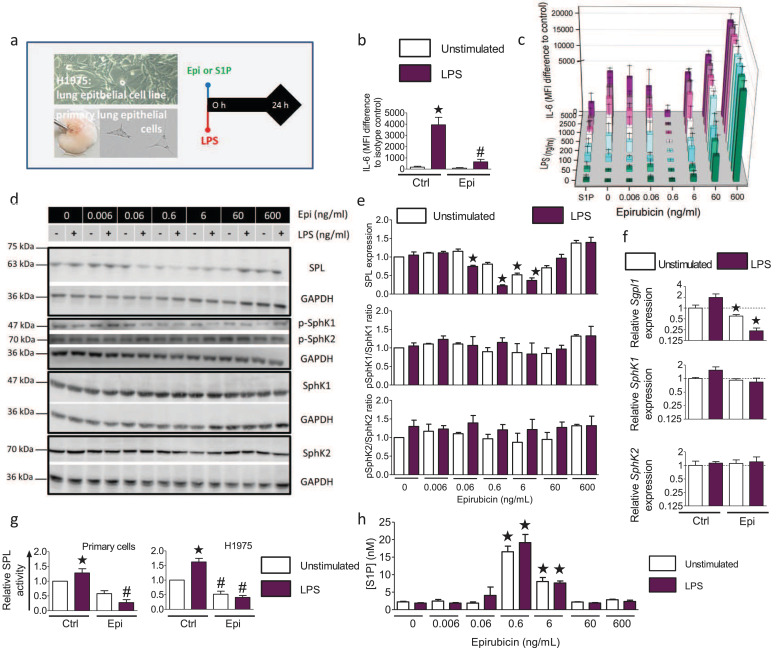
Fig. 2.
Protective effect of low-dose epirubicin on LPS–induced inflammatory responses of lung epithelial cells depends on downregulation of S1P lyase and subsequent S1P release.
(a) Experimental protocol: Primary mouse lung epithelial cells and H1975 cells were stimulated for 24 h with 200 ng/ml LPS and indicated concentrations of epirubicin (Epi). (b) IL-6 production of primary lung epithelial cells ± 0.6 ng/ml Epi and 200 ng/ml LPS n = 3–5, *p<0.05 to unstimulated, #p<0.05 to LPS (unpaired, two-tailed t-test). (c) IL-6 production in H1975 cells treated with indicated concentrations of Epi and LPS ± 0.5 µM S1P, mean ± SEM,n = 3–5, p<0.05 for all treatments with 200 ng/ml LPS or higher compared to untreated control except for cells treated with S1P or 0.6 ng/ml Epi (One-way ANOVA with Bartlett´s test for equal variances and post-hoc Bonferroni's multiple comparison test). (d) Western Blot analysis of SPL, SphK1, SphK2 and p-SphK1 and p-SphK2 levels in H1975 cells stimulated as indicated. (e) Densitometric quantification of data shown in (d), means ± SEM, n = 3–5. (f) mRNA expression of SPL, SphK1 and SphK2 was determined by qPCR in H1975 without or with 0.6 µg/ml Epi and normalized to HPRT, *p<0.05 to untreated control, n = 3 (Pair‐wise fixed reallocation randomization test). (g) SPL activity in cell lysates of primary murine lung epithelial cells (left) and H1975 cells (right) stimulated for 24 h without or with LPS and 0.6 ng/ml Epi, mean ± SEM, n = 5, *p<0.05 compared to unstimulated control (One-way ANOVA with Bartlett test for equal variances and post-hoc Bonferroni for multiple comparisons), #p < 0.05 compared to LPS-stimulated cells without Epi (Two-tailed, unpaired t-test). (h) S1P secretion in H1975 cells treated for 24 h without or with LPS and indicated concentrations of Epi, mean ± SEM, *p<0.05 n = 3–6 (One-way ANOVA with post-hoc Bonferroni's multiple comparison test to unstimulated control cells).