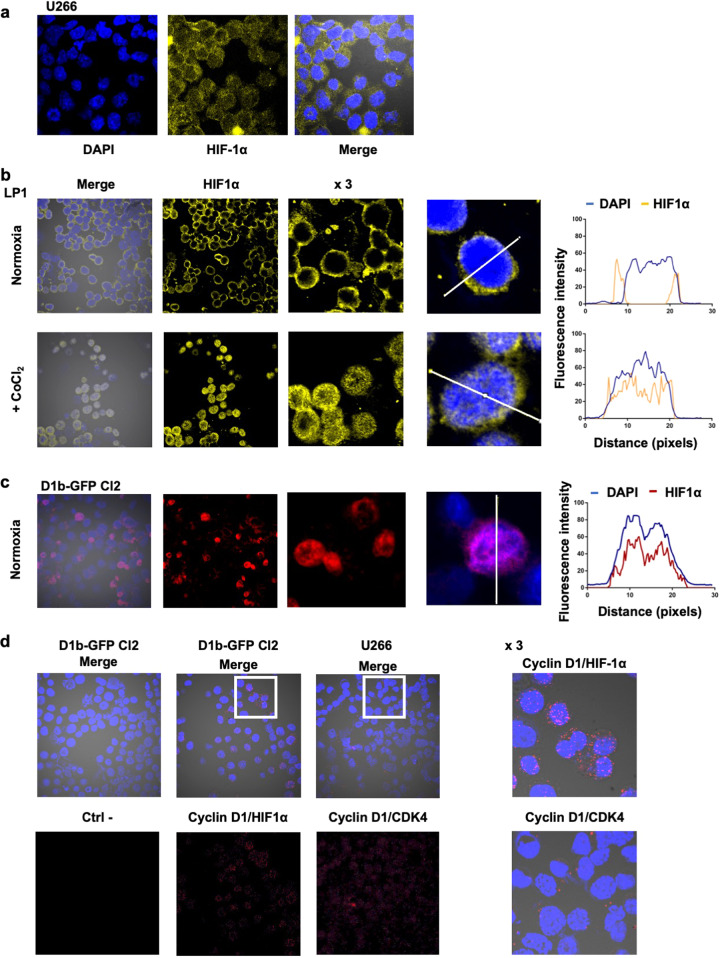
Fig. 4. The nuclear form of cyclin D1 binds HIF1α.
a U266 cells were cultured under normoxia and analyzed by IF and confocal microscopy after DAPI (in blue) or HIF1α (in yellow) staining (×180 magnification). b LP1 cells were cultured under normoxia or treated with 300 μM CoCl2 overnight and analyzed after DAPI (in blue) or HIF1α (in red) staining. Merged images of representative cells were processed with ImageJ software, and the curves of FI as a function of distance were exported. c D1b–GFP Cl2 cells were cultured under normoxia and analyzed by IF, as previously described. d Duolink PLA technology was used on D1b–GFP Cl2 cells treated with CoCl2 (to enhance the signal) and U266 cells (as a control), to investigate cyclin D1/HIF1α and cyclin D1/CDK4 interactions, respectively. Slides were incubated with the primary Abs, except for the negative control (Ctrl−), and then with the secondary Abs conjugated to the MINUS and PLUS probes. The slides were counterstained with DAPI before confocal microscopy examination (×180 magnification). Representative fields (white squares) were enlarged (×3).