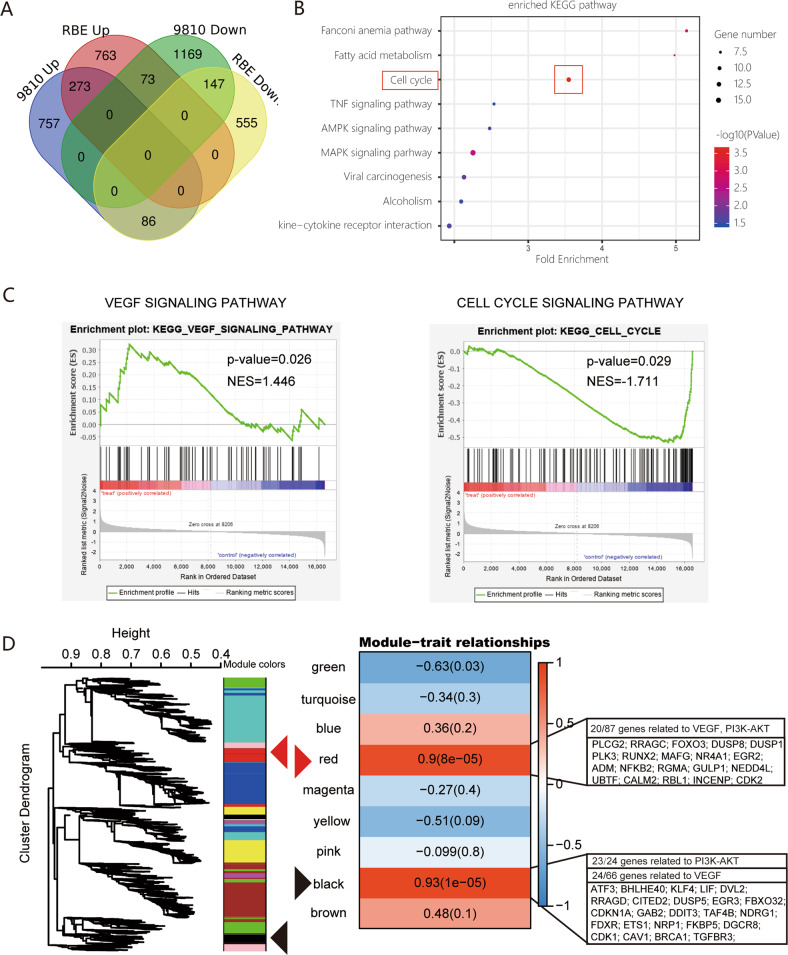
Fig. 4. Transcriptome analysis indicates the effect of anlotinib in ICC is via the VEGF/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.
a Venn diagram revealed the common up/downregulated genes (adjusted P value < 0.05, fold-change = 2) detected using RNA-seq in HCCC9810 and RBE cells treated with anlotinib; 420 genes were shared in the two cell lines (273 genes upregulated, 147 genes downregulated); b KEGG enrichment analysis based on these differentially expressed genes; c gene set enrichment analysis of mRNA expression profiles of the two cell lines revealed that cell cycle and VEGF signaling pathways were significantly altered after anlotinib treatment of ICC cells; d a weighted gene co-expression network analysis algorithm was implemented to construct the gene co-expression network. The module–trait relationships revealed two modules highly correlated with anlotinib treatment phenotype: the black module (correlation: 0.93, P < 0.01) and the red module (correlation: 0.90, P < 0.01). Pathway annotation showed that the genes in these two critical modules were mainly enriched in the VEGF signaling network and PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.