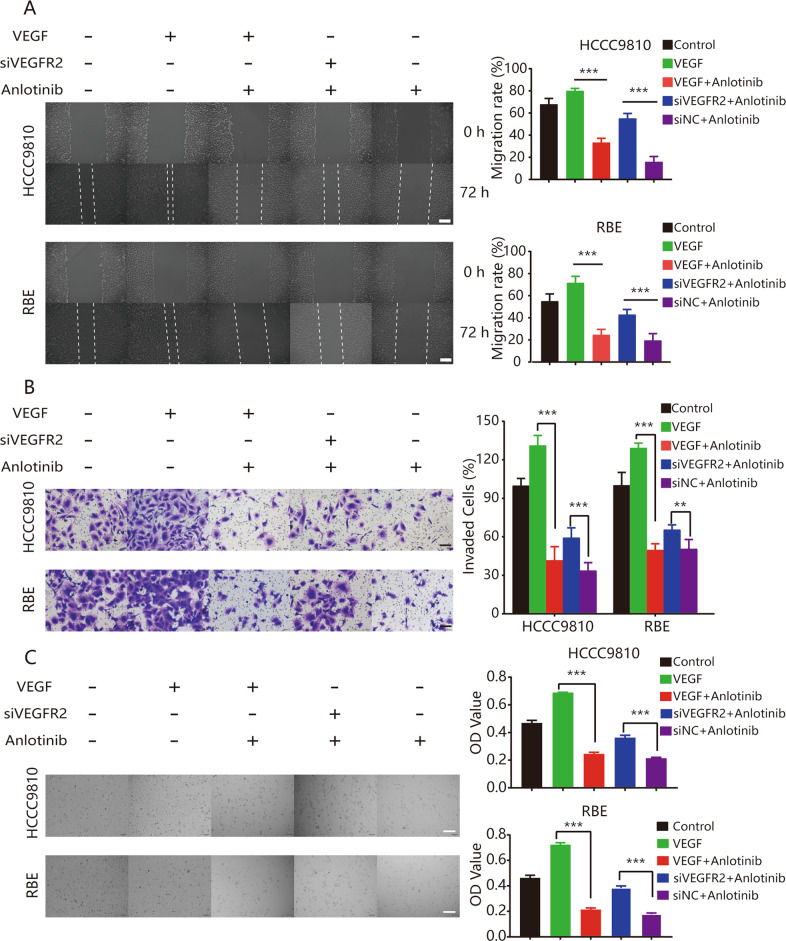
Fig. 6. Antitumor activity of Anlotinib was mainly dependent on VEGFR2 expression.
a Wound-healing assays showed the effects of VEGFR2 expression on the anti-migration ability of anlotinib. Representative images of migration are shown in the left panel. Degrees to which wounds healed in the indicated groups are shown in the histogram. Significantly decreased inhibition effects on migration of anlotinib were observed when VEGFR2 was silenced in HCCC9810 and REB ICC cells lines; b transwell assays revealed the effects of VEGFR2 expression on the anti-invasion ability of anlotinib. Inhibition effects of anlotinib were significantly reduced when VEGFR2 expression was knocked down. The histogram shows the relative proportions of invading cells; c CCK8 experiments were performed to confirm the effects of VEGFR2 in anlotinib-induced inhibition of proliferation. When VEGFR2 expression was knocked down, anlotinib’s antiproliferative ability was significantly reduced. Representative images were photographed using an inverted microscope and are shown in the left panel. The histogram shows the OD values for each group after 48 h of drug treatment. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. Scale bars = 100 μm.