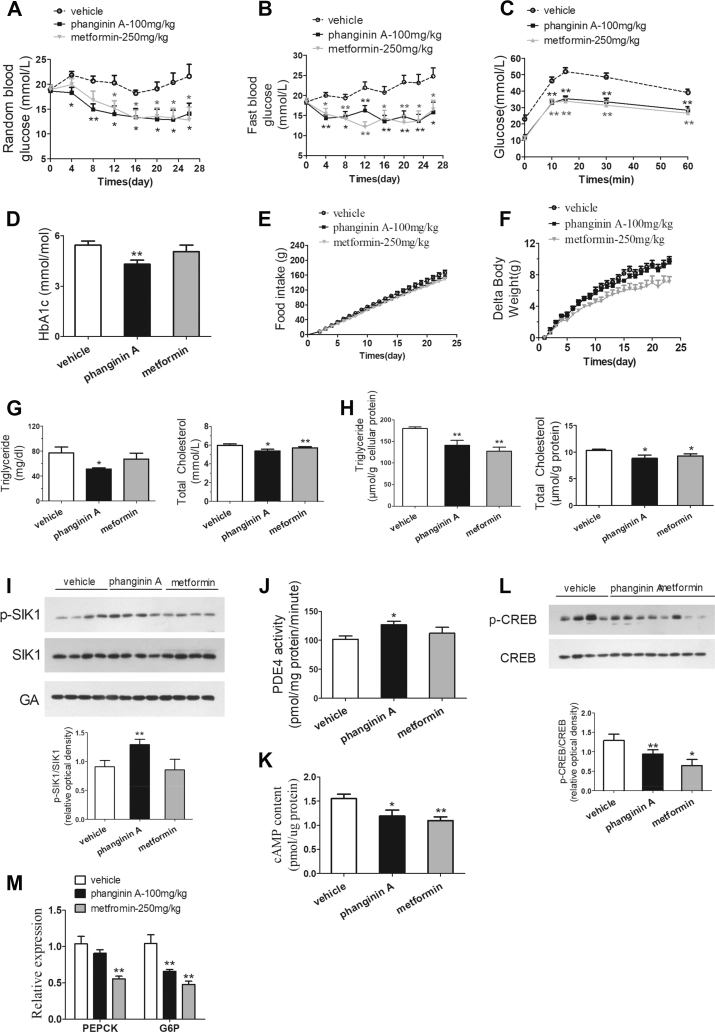
Figure 8.
Chronic treatment of phanginin A improved metabolic disorders in ob/ob mice. Male ob/ob mice were treated with phanginin A (100 mg/kg, once daily, p. o.), metformin (250 mg/kg, once daily, p. o.), or vehicle for 26 days. (A–B) Random (A) and fasting blood glucose levels (B) were detected on days 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 23, and 26. (C) Oral glucose tolerance tests were conducted on day 23. (D) HbA1c was determined on day 26. (E–F) Food intake accumulation (E) and body weight (F) were regularly measured during treatment. (G–H) Triglyceride and total cholesterol in the serum (G) and liver (H) were detected. (I) SIK1 phosphorylation in the liver was analyzed by Western blotting and quantified as the relative optical density. (J) Hepatic PDE4 activity and (K) cAMP concentration were examined after treatment. (L) CREB phosphorylation in the liver was analyzed by Western blotting. (M) Hepatic gluconeogenesis gene expression in ob/ob mice were evaluated. All of the results are presented as the mean ± SEM (n = 8). ∗P < 0.05 and ∗∗P < 0.01 vs the vehicle group.