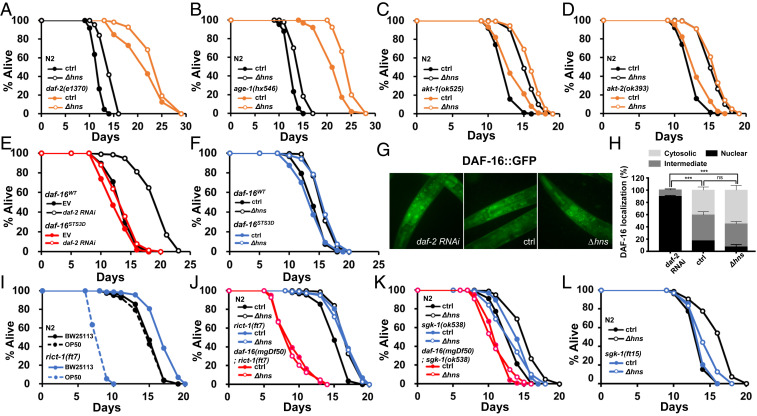
Fig. 4.
Δhns E. coli modulate longevity through TORC2/SGK-1. (A–D) IIS is not involved in lifespan regulation in Δhns E. coli. Δhns E. coli significantly extended lifespan in daf-2(e1370) (A), age-1(hx546) (B), akt-1(ok525) (C), and akt-2(ok393) (D) mutants. (E and F) The daf-16STS3D transgene did not rescue the lifespan extension by daf-2 RNAi (E) but fully rescued the lifespan extension by Δhns E. coli (F). (G and H) Compared with control, nuclear localization of DAF-16 was enhanced by daf-2 RNAi (***P < 0.001, Fisher’s exact test; n = 23), but not by Δhns E. coli (P = 0.6151, Fisher’s exact test; n = 23). Error bars indicate SEM. Results from one of three independent experiments are shown. (I) Lifespan of C. elegans on standard E. coli B strain OP50 and E. coli K12 strain BW25113. C. elegans rict-1(ft7) mutants lived significantly longer on the BW25113 strain compared with OP50. Wild-type N2 exhibited comparable lifespans irrespective of E. coli strain. (J and K) TORC2/SGK-1 is critical for lifespan modulation by Δhns E. coli. Δhns E. coli did not further extend the lifespan of rict-1(ft7) (J) or sgk-1(ok538) (K) mutants. daf-16(mgDf50) suppressed the long lifespan of rict-1(ft7) (J) or sgk-1(ok538) mutants (K). (L) Lifespan extension was attenuated in sgk-1 gain-of-function mutant sgk-1(ft15).