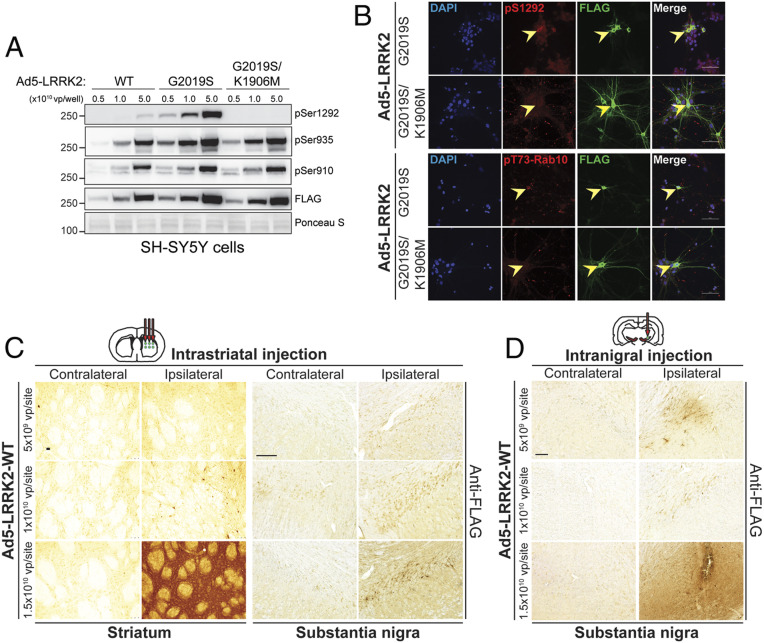
Fig. 1.
Evaluation of Ad5 vector infectivity in rat brain via distinct delivery paradigms. (A) Validation of new high-titer Ad5-LRRK2 (WT, G2019S, and G2019S/K1906M) vectors and LRRK2 phosphorylation in SH-SY5Y cells. Cells were transduced with increasing viral particles of each Ad5-LRRK2 vector (0.5, 1, or 5.0 × 1010 vp/well). Western blot analysis of cell extracts with FLAG antibody (transduced human LRRK2) or antibodies to detect LRRK2 autophosphorylation (pSer1292) or constitutive phosphorylation (pSer935, pSer910) sites to detect a titer-dependent increase in human LRRK2 levels/activity. Ponceau S stain was used as a protein loading control. Molecular mass markers are indicated in kilodaltons. (B) Immunofluorescent colocalization analysis in primary cortical neurons infected with Ad5-LRRK2 vectors (1.5 × 1010 vp/dish) at DIV3 and fixed at DIV6. Arrowheads indicate cortical neurons expressing human LRRK2 (FLAG, green), their corresponding signal for pS1292-LRRK2 or pT73-Rab10 (red), and merged images. (Scale bar: 50 µm.) (C) Evaluation of Ad5-LRRK2 vectors following intrastriatal delivery with increasing viral titer (0.5, 1, or 1.5 × 1010 vp/site, at 2.5 μL/site) at six distinct injection sites. Immunohistochemistry showing dose-dependent expression of human LRRK2-WT (anti-FLAG antibody) in the ipsilateral rat striatum and substantia nigra at 10 d postinjection. (Scale bars: 500 μm.) (D) Evaluation of Ad5-LRRK2 vectors following intranigral delivery with increasing viral titer (0.5, 1, or 1.5 × 1010 vp/site, in 2.5 μL) at a single injection site. Immunohistochemistry showing dose-dependent expression of human LRRK2-WT (anti-FLAG antibody) in rat substantia nigra at 10 d postinjection. (Scale bars: 500 μm.)