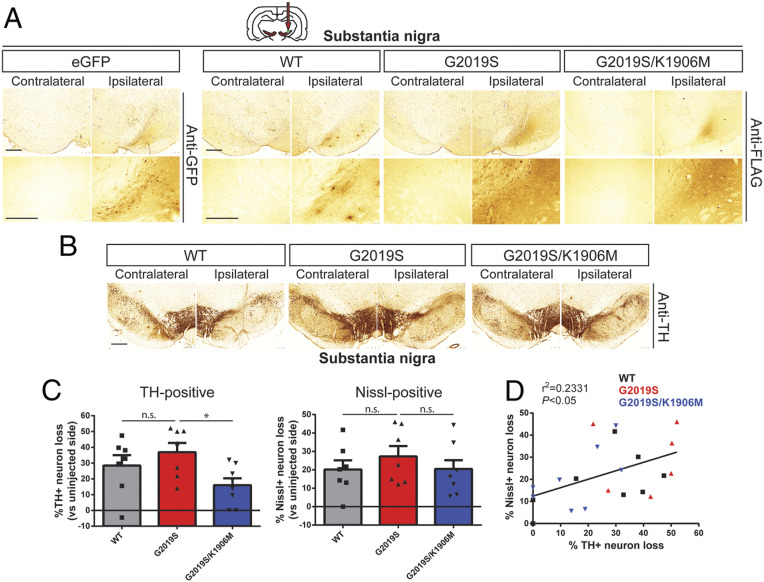
Fig. 2.
Intranigral delivery of Ad5-LRRK2-G2019S induces dopaminergic neurodegeneration in a kinase-dependent manner in adult rat brain. (A) Ad5-LRRK2 (WT, G2019S, or G2019S/K1906M) vectors were unilaterally delivered at a single site (1.5 × 1010 vp/site, in 2.5 μL) in the rat substantia nigra. Immunohistochemistry reveals expression of eGFP (anti-GFP antibody) or human LRRK2 variants (anti-FLAG antibody) that persists up to 21 d postinjection. Images indicate low and high magnification for each vector. (Scale bars: 500 μm.) (B) Immunohistochemistry revealing dopaminergic neurons (anti-TH antibody) in contralateral and ipsilateral substantia nigra at 21 d postdelivery of Ad5 vectors. (Scale bars: 500 μm.) (C) Unbiased stereological analysis of TH-positive dopaminergic and total Nissl-positive neuron number in the substantia nigra at 21 d postinjection. Bars represent % neuronal loss in the injected ipsilateral nigra relative to the contralateral nigra (mean ± SEM, n = 7 to 8 animals/vector), *P < 0.05 by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test; n.s., nonsignificant. (D) Linear regression analysis indicating a significant positive correlation between TH-positive and Nissl-positive neuron loss in the substantia nigra. Data points represent individual animals. Pearson’s correlation coefficient, r2 = 0.2331, P < 0.05.