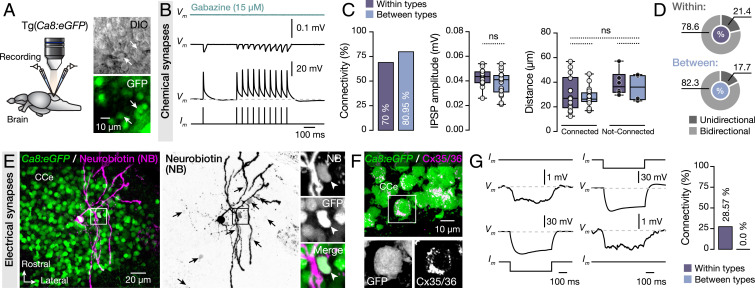
Fig. 2.
Synaptic interactions between adult zebrafish Purkinje cells. (A) Ex vivo setup of isolated intact brain from Tg(Ca8:eGFP) line allows simultaneous dual recordings of Purkinje cells. Arrows indicate the recorded cells. (B) Representative average (from ∼40 sweeps) sample traces from paired Purkinje cell recordings show small but robust monosynaptic IPSPs. All IPSPs were blocked by applying selective GABAA receptor antagonist gabazine (15 μM). (C) Quantification of the observed connectivity between Purkinje cells (Connected: within types, 14 of 20; between types, 17 of 21). Quantification of the connectivity strength (IPSP amplitude) and the relative distance between connected and not-connected pairs of Purkinje cells were all not significant regardless of type. (D) Proportions of unidirectional and bidirectional connections between Purkinje cells of the same type (Within) and different type (Between). (E) Single Purkinje cell neurobiotin injection (magenta) in Ca8:GFP line (green) resulted in dye coupling of other Purkinje cells (black arrows). Arrowheads indicate a dye coupled neuron (NB+) as Purkinje cell (GFP+). (F) Detection of Cx35/36 puncta (magenta) on Purkinje cell bodies (green). In Inset, a magnification of a representative example of Purkinje cell soma (GFP+) decorated with connexins puncta (Cx35/36). (G) Sample recordings showing bidirectional electrical coupling only in chemically connected Purkinje cells of the same type (4 of 14 connected pairs). CCe, corpus cerebelli; Cx, connexin; DIC, Differential interference contrast; GFP, green fluorescent protein; IPSP, inhibitory postsynaptic potential. Data are presented as box plots showing the median with 25/75 percentile (box and line) and minimum–maximum (whiskers). ns, not significant. For detailed statistics, see SI Appendix, Table S1.