Figure 3. Two interfaces mediate hCASP1 engagement of mGSDMD.
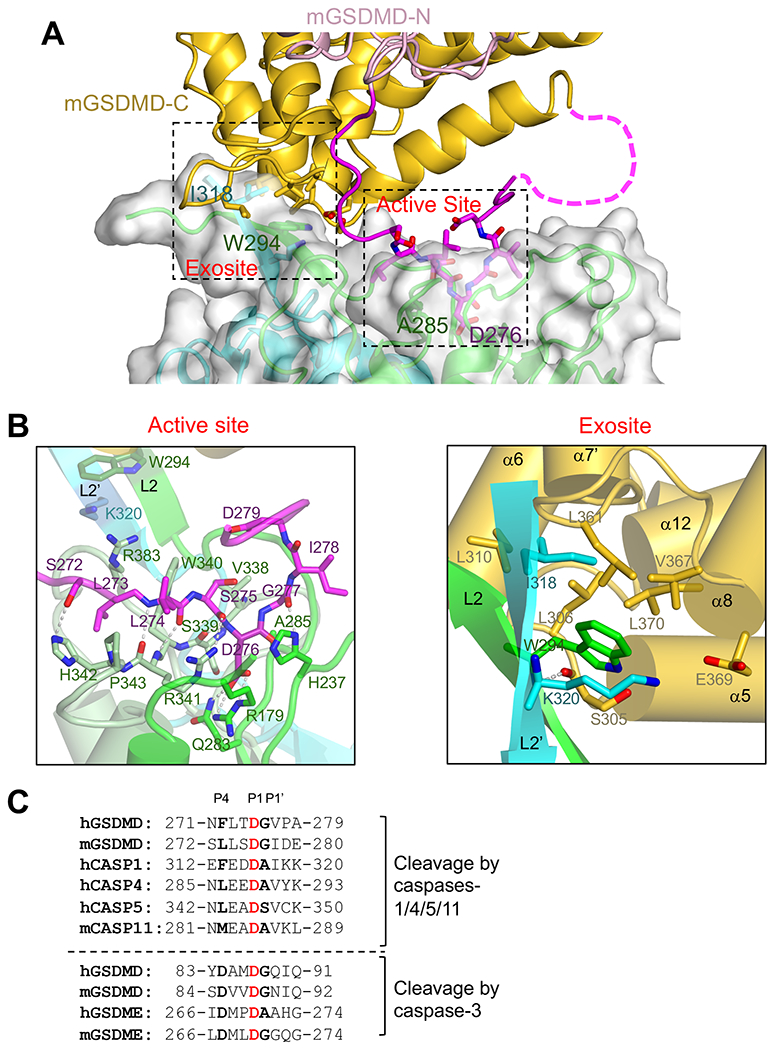
(A) A view of the dual interface between hCASP1 and mGSDMD, with the same color scheme as figure 2A. The CASP1 dimer is shown as both ribbons and transparent surface. The view is approximately 180 degrees from that in figure 2A.
(B)Left panel is a close-up view of the hCASP1-mGSDMD interface at the active site with the GSDMD linker colored magenta, and CASP1 colored green for p22, pale-green and cyan for p10 subunits, respectively. Residues participating in this interface, as well as residues W294 and K320 at the exosite, are shown in ball-and-sticks. Hydrogen bonds are shown as gray dotted lines.
Right panel is a close-up view of the hCASP1-mGSDMD interface at the exosite. The GSDMD-CTD is colored gold. The L2 and L2’ strands are colored green and cyan, respectively. The mainchain hydrogen bond between W294 in hCASP1 and S305 in mGSDMD is shown as a gray dotted line.
(C) The inflammatory caspase cleavage sites in GSDMD and caspases-1,4, 5, and 11 are shown above the dotted line. The caspase-3 cleavage sites in GSDMD and GSDME are shown below the dotted line for comparison. Identical residues at the P1 sites are in red, and conserved residues at the P4 and P1’ sites are in bold.
See also Figure S3.
