Fig. 2. Shisa7 binds GABAARs through a distinctive N-terminal domain and controls synaptic abundance of GABAARs.
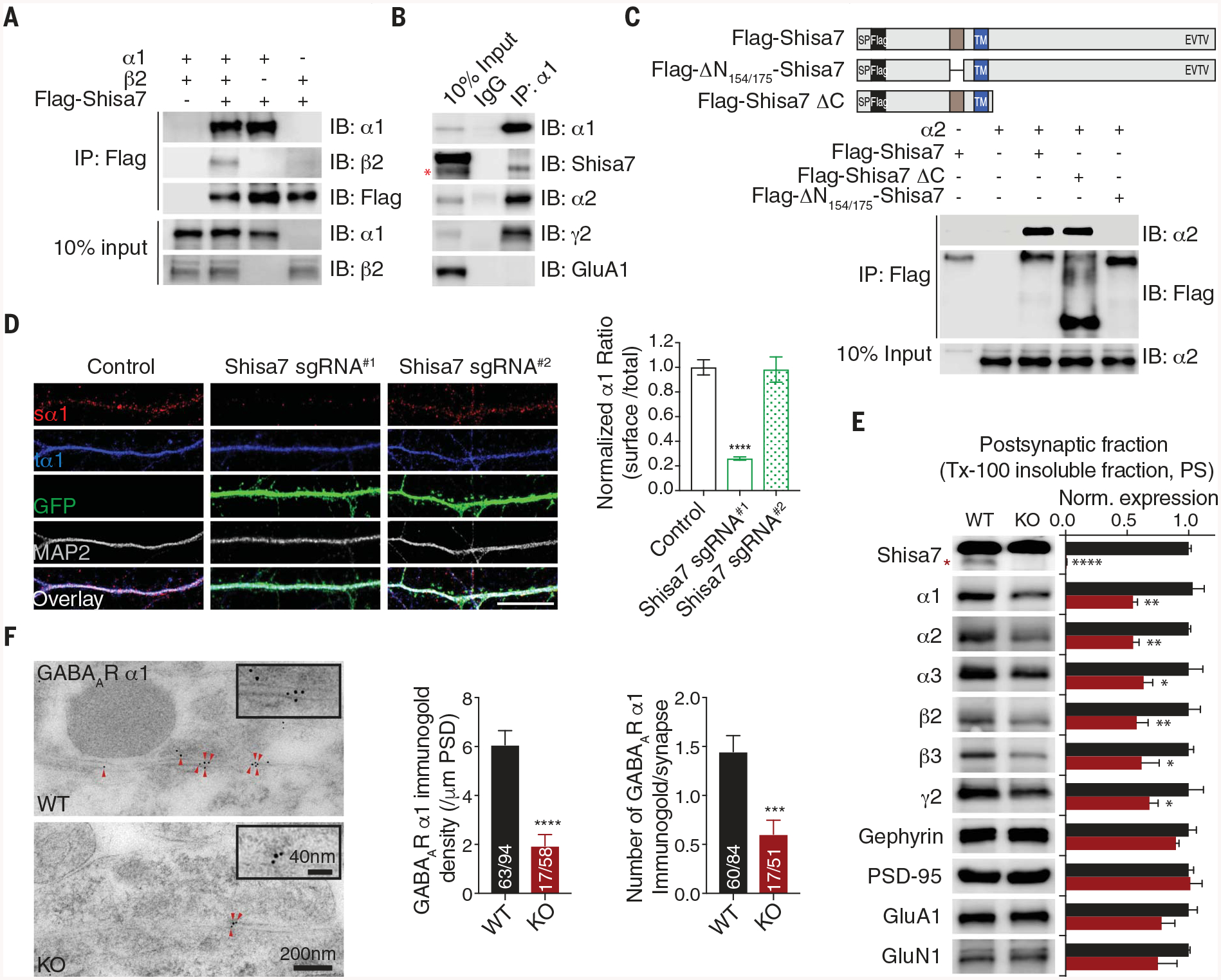
(A nd B) The α1 subunit coimmunoprecipitated with Shisa7 in HEK cells (A) and in hippocampal lysates (B). IB, immunoblot; IgG, immunoglobulin G. (C) Schematic of Flag-Shisa7, Flag-ΔN154/175-Shisa7, and Flag-Shisa7ΔC. SP, signal peptide; TM, transmembrane domain. In HEK cells, the α2 subunit coimmunoprecipitated with Flag-Shisa7 and Flag-Shisa7ΔC but not Flag-ΔN154/175-Shisa7. (D) Expression of Shisa7 sgRNA#1, but not sgRNA#2, in hippocampal neurons reduced the ratio of surface α1 (sα1) and total α1 (tα1). Control n = 39; sgRNA#1 n = 21; sgRNA#2 n = 18. A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used. Scale bar, 10 mm. (E) Protein expression in postsynaptic fractions (PS) from Shisa7 WT and KO mice (n = 5 for both conditions; one-way ANOVA was used). Tx-100, Triton X-100. (F) Postembedding immunogold labeling of the α1 subunit in the hippocampal CA1 region showed that Shisa7 KO significantly reduced the density of α1 at the inhibitory postsynaptic density (PSD). Data for α1 density (control n = 63/94, KO n = 17/58) and data for immunogold labeling per synapse (control n = 60/84, KO n = 17/51) were evaluated with a t test. Scale bar, 200 nm (low-magnification images) or 40 nm (high-magnification images). The red asterisk indicates the Shisa7 band. Error bars indicate SEM. ****P < 0.0001; ***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05.
