Fig. 4. Shisa7 KO diminishes DZ effects in vitro and in vivo.
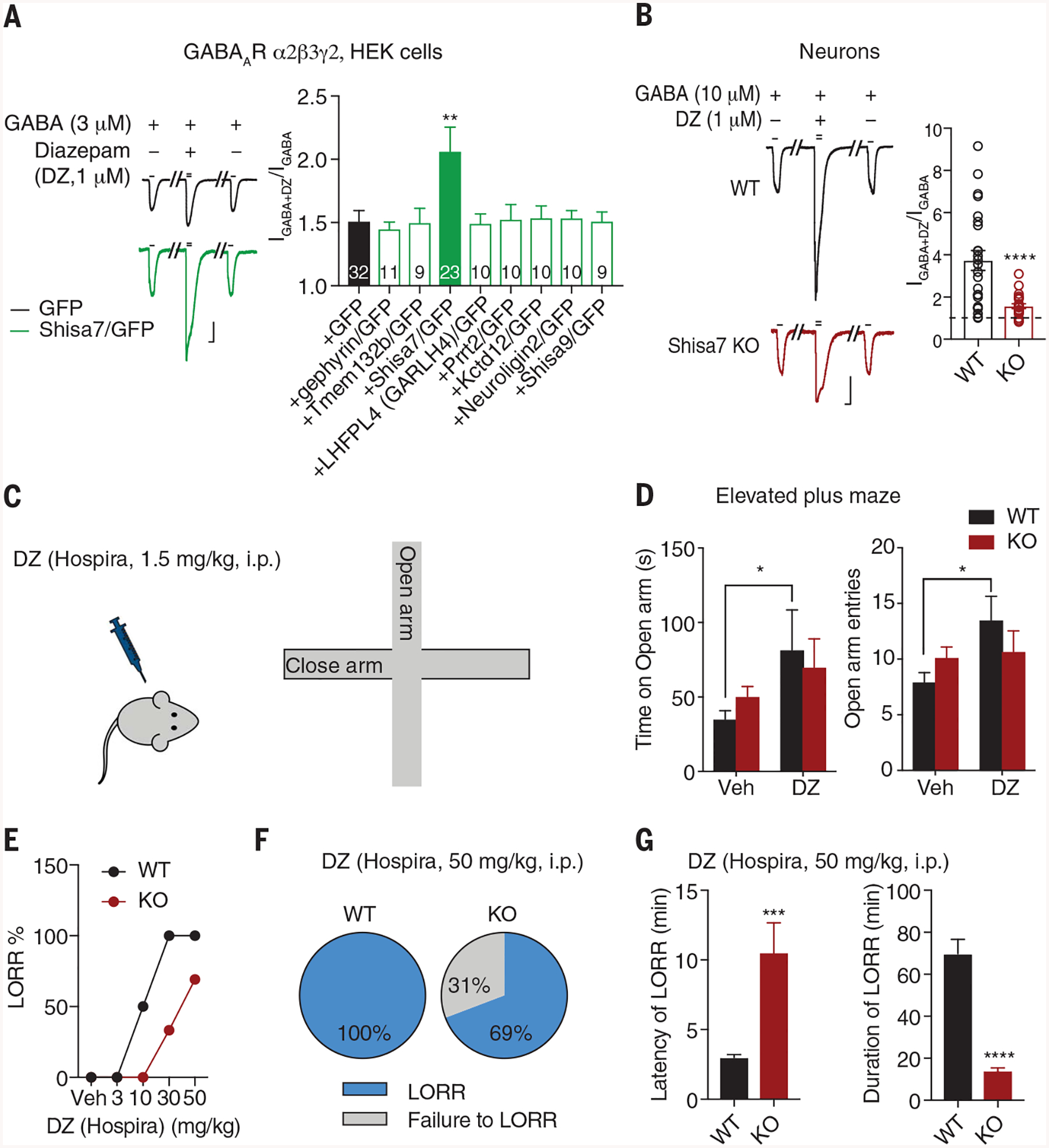
(A) Shisa7, but not other molecules, potentiated the DZ effect on GABA response of α2β3γ2 in HEK cells (one-way ANOVA). Scale bar, 200 pA, 2 s. (B) Shisa7 KO significantly reduced DZ-induced potentiation of GABA-evoked whole-cell currents in cultured neurons (WT n = 24; KO n = 23; t test). Scale bar, 500 pA, 2 s. (C and D) DZ (1.5 mg/kg) increased the time spent on open arm and the number of open arm entries in WT mice but not Shisa7 KO mice. Veh, vehicle. (Treatment groups: Veh WT n = 14 and KO n = 21; DZ WT n = 10 and KO n = 15.) Time: treatment [F1,56 = 5.113, P < 0.05]; group [F1,56 = 0.016, P > 0.05]; treatment × group [F1,56 = 0.845, P > 0.05]; entries: treatment [F1,56 = 4.501, P < 0.05]; group [F1,56 = 0.035, P > 0.05]; treatment × group [F1,56 = 3.101, P > 0.05]; two-way ANOVA. (E) Dose-response relationship of DZ in LORR [Veh n = 6 for both conditions; DZ (3 mg/kg) n = 6 for both conditions; DZ (10 mg/kg) WT n = 6 for both conditions; DZ (30 mg/kg) WT n = 7, KO n = 6; DZ (50 mg/kg) WT n = 13 for both conditions). (F) DZ at the hypnotic dose produced LORR in 100% of WT mice (n = 13), but only 69% of KO mice (9 of 13 mice). (G) Shisa7 KO significantly prolonged latency to LORR and shortened duration of LORR after DZ administration (WT n = 13, KO n = 9; t test). Error bars indicate SEM. ****P < 0.0001; ***P < 0.001; **P < 0.01; *P < 0.05.
