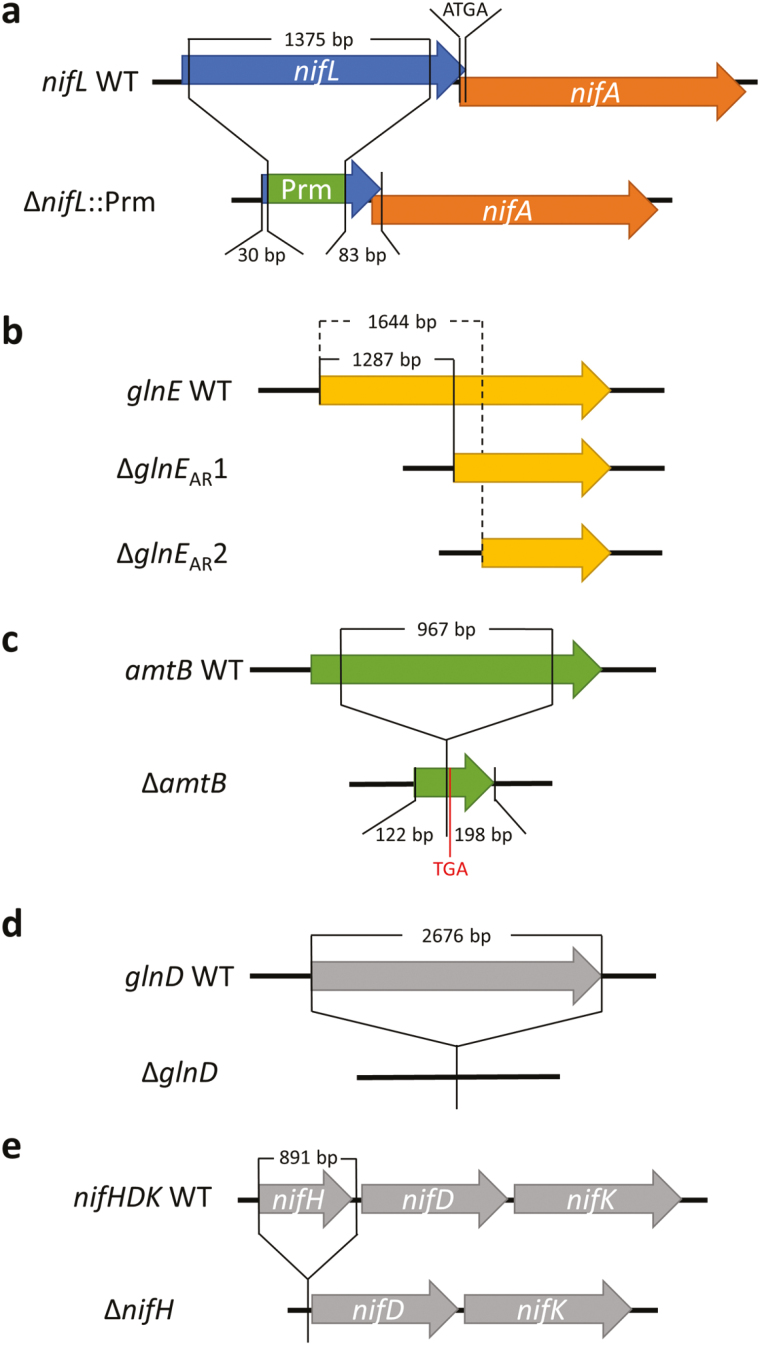
Fig. 2.
Mutated sequences of the key genes of the nitrogen fixation and assimilation regulatory network of PBC6.1. (a) Representation of the ΔnifL::Prm mutations. The majority of the nifL gene was disrupted, leaving some nucleotides at the 5' and 3' ends. The start codon of nifA, which overlaps with the stop codon of nifL, was left intact. Promoter (Prm) sequences from two different loci in the PBC6.1 genome were inserted into the disrupted portion of the nifL gene to drive nifA transcription. (b) Representation of the ΔglnEAR mutations. The 5' region of the glnE gene was deleted, to remove the N-terminal adenylyl-removing (AR) domain of the resulting protein. A start codon was re-inserted at the 5' end of the truncated sequences to allow protein translation. (c) Representation of the ΔamtB mutation. The majority of the amtB gene was deleted, leaving some nucleotides at the 5' and 3' end. The deletion resulted in a frameshift, causing a stop codon just after the point of deletion. (d) Representation of the ΔglnD mutation. The entire coding region of the glnD gene was deleted, starting at the A of the ATG start codon and ending immediately after the gene’s stop codon. No flanking regions were deleted. (e) Representation of the nifHDK operon and the ΔnifH mutation. The entire nifH coding region was deleted starting at the A of the ATG start codon and ending 9 bp downstream of the stop codon.