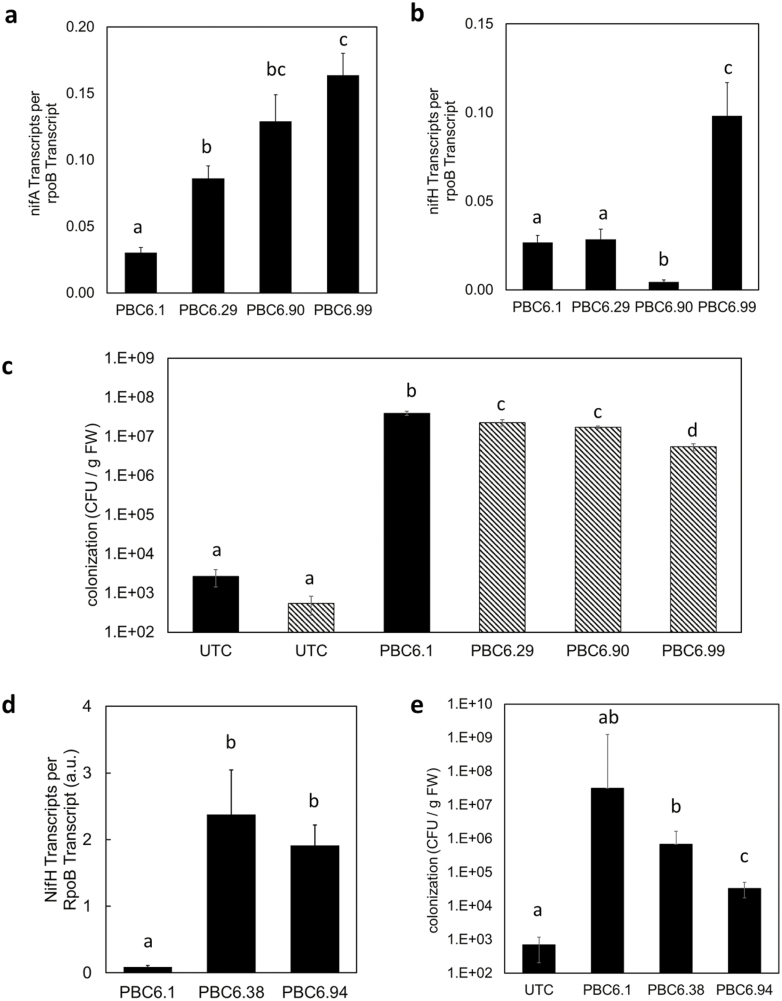
Fig. 5.
Greenhouse experiments demonstrate rhizosphere nifH transcription in fertilized corn. (A–C) Corn was planted in a controlled-environment growth chamber and inoculated with PBC6.1, PBC6.29, or PBC6.99. Upon the emergence of the second leaf collar, plants were harvested, and nucleic acids were extracted from the rhizosphere to quantify nifA (A) and nifH (B) transcript levels and colonization (C) of each strain. Data are presented as the mean of five root samples pooled from five plants each. (D and E) In a second experiment, 4 weeks after inoculation with PBC6.1 derivative strains, the corn root-associated microbiome was extracted. (D) In planta transcription of nifH was measured. The remodeled strains showed higher nifH transcription than PBC6.1 in the corn root environment. Error bars show the SE of the mean of at least three biological replicates. (E) Colonization is reported as the geometric means of at least eight biological replicates. In (C) and (E), black bars represent samples analyzed using primers targeting the nifH–por2 intergenic region, and hatched bars represent samples analyzed using primers targeting the ∆nifL::Prm5 genotype. Error bars show the SE of the mean. Within each panel, letters indicate groups for which P was <0.05 according to a two-tailed, two-sample unequal variance t-test.