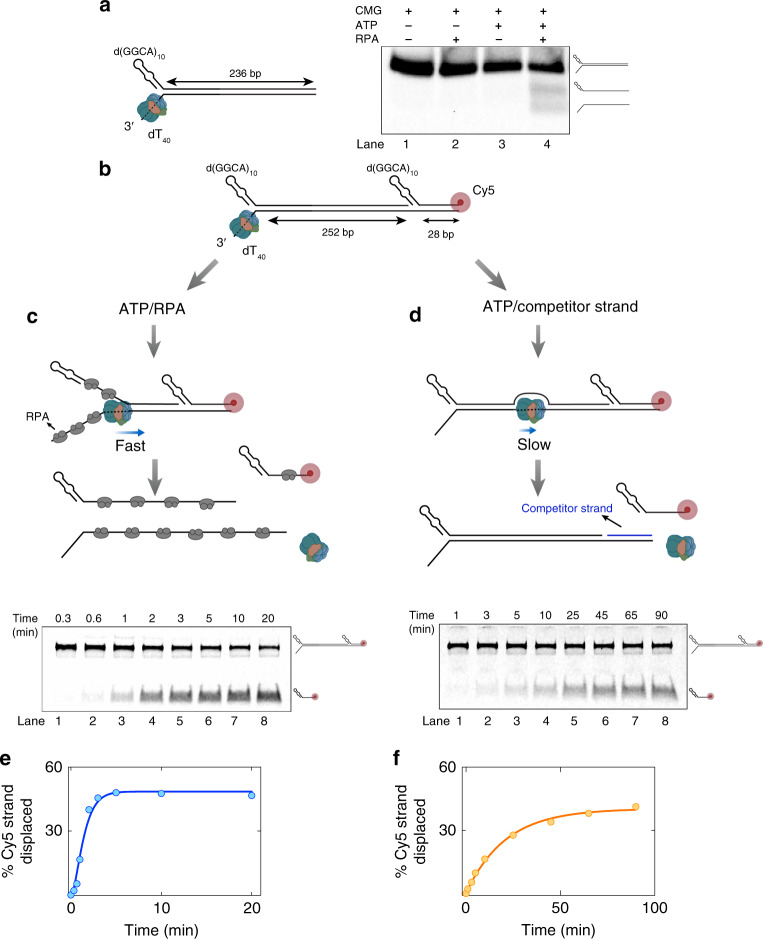
Fig. 2. RPA increases the rate of DNA unwinding by CMG.
a Fork DNA containing 236-bp dsDNA was incubated with CMG in the presence of ATPγS for binding to 3′ dT40 tail. ATP was added with (lane 4) or without (lane 3) RPA and incubated further before separating on 3% agarose. DNA was labeled internally with multiple Cy5 fluorophores on both strands. This experiment was performed once. b Fork DNA substrate containing 252-bp long dsDNA, followed by 28-bp duplex and Cy5-modification on the excluded strand was bound by CMG. ATP was added to initiate translocation by the helicase. c CMG-mediated displacement of Cy5-labeled strand in the presence of RPA. When included in ATP buffer, RPA prevents reannealing of DNA behind the helicase as well as new CMG binding. d CMG-mediated displacement of Cy5-labeled strand in the absence of RPA. DNA rewinds within the 252-bp duplex region. To prevent rehybridization of the Cy5-labeled strand to long DNA substrate, excess competitor oligonucleotide containing complementary 28-nt sequence to long DNA was added with ATP. To achieve single-turnover kinetics, excess dT40 oligonucleotide was included in ATP buffer that captures any free CMG. e, f Percentage of Cy5-modified strand displaced versus time by CMG in the presence e and absence of RPA f. The data in c–f represent mean from n = 2 independent experiments, and were fit to Eq. (1) with m = 1 or 2 (see Methods) resulting in best R2 value. Solid lines are fits to Eqs. (2) and (3) in e and f, respectively. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.