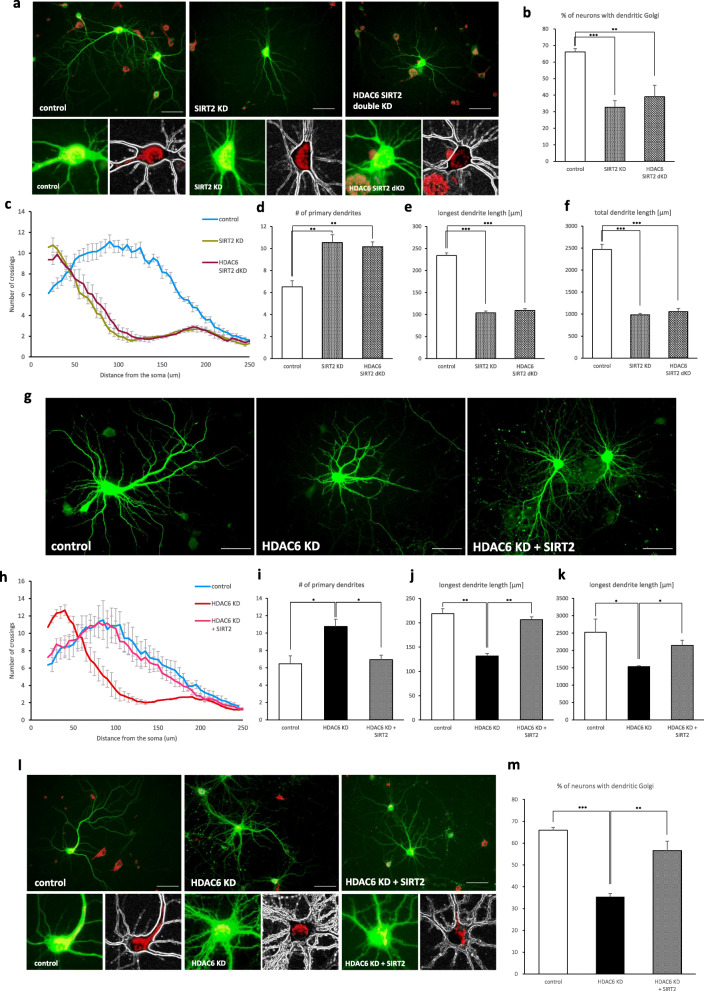
Fig. 5.
SIRT2 compensates for the function of HDAC6 in hippocampal neurons. a-f SIRT2 single knockdown or HDAC6 SIRT2 double knockdown was defective in dendrite development and Golgi polarization. a Phenotype of SIRT2 knockdown or HDAC6 and SIRT2 double knockdown neurons. The Golgi apparatus was stained by GM130 (red). Scale bar, 50 μm. b Graphs showing the percentage of neurons with dendritic Golgi. Data represents average of three independent experiments (n = 60–80 for each group in each experiment). c Sholl graphs represent the number of crossing in SIRT2 knockdown neurons and HDAC6 and SIRT2 double knockdown neurons. Data represents average of three independent experiments (n = 10 for each group in each experiment). d-f Quantification of the primary dendrites (d), longest dendrite length (e), and total dendrite length (f). g-m HDAC6 knockdown neurons rescued the phenotype when expressing SIRT2 cDNA. g HDAC6 shRNA expressing neurons affected dendrite development. Expression of SIRT2 rescued the HDAC6 knockdown phenotype of hippocampal neurons. Scale bar, 50 μm. h Sholl graphs of neurons expressing Venus or HDAC6 shRNA or HDAC6 shRNA together with SIRT2. Data represents average of three independent experiments (n = 10 for each group in each experiment). i-k Quantification of the number of primary dendrites (i), longest dendrite length (j), and total dendrite length (k). l Expression of SIRT2 rescued the HDAC6 knockdown phenotype of hippocampal neurons in Golgi polarization. The Golgi apparatus was stained by GM130 (red). Scale bar, 50 μm. m Quantification of the percentage of neurons with dendritic Golgi. Data represents average of three independent experiments (n = 40–60 for each group in each experiment). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 by two-tailed Student’s t-test. The symbol # represents the number. Error bar means ± S.E.M. in all graphs