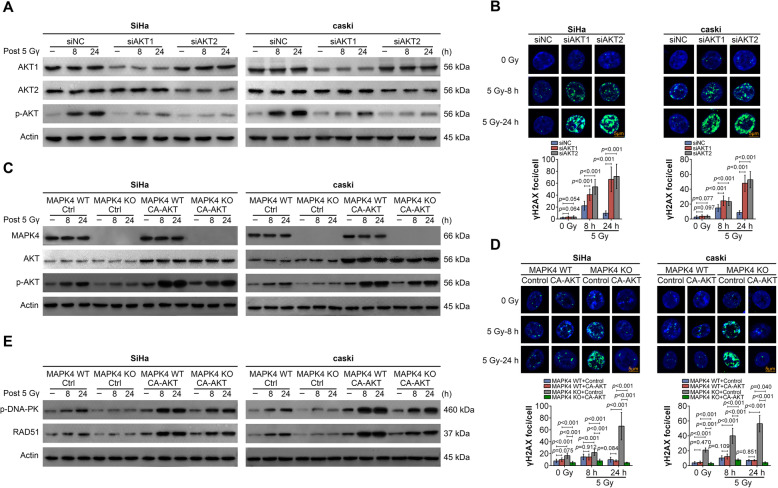
Fig. 4.
MAPK4 affects the sensitivity of cervical cancer cells to radiation by regulating AKT phosphorylation. a Relative protein levels of AKT1, AKT2 and p-AKT in SiHa or caSki cells after transfecting siNC, siRNAs for AKT1 or AKT2 at 0 h, 8 h and 24 h, as determined using western blotting. b The γH2AX levels in SiHa or caSki cells after transfecting siNC, siAKT1 or siAKT2 at 0 h, 8 h and 24 h, as determined using immunofluorescence. Fluorescence intensity was quantified and shown as histogram (Scale bar, 5 μm). c Relative protein levels of MAPK4, AKT and p-AKT in SiHa or caSki MAPK4 WT cells and MAPK4 KO cells after transfecting Ctrl or CA-AKT at 0 h, 8 h and 24 h, as determined using western blotting. d The γH2AX levels in SiHa or caSki cells after transfecting siNC, siAKT1 or siAKT2 at 0 h, 8 h and 24 h, as determined using immunofluorescence. Fluorescence intensity was quantified and shown as histogram (Scale bar, 5 μm). e Relative protein levels of p-DNA-PK and RAD51 in SiHa or caSki MAPK4 WT cells and MAPK4 KO cells after transfecting Ctrl or CA-AKT at 0 h, 8 h and 24 h, as determined using western blotting. Representative images of three independent experiments were shown. Data are expressed as the mean ± SEM