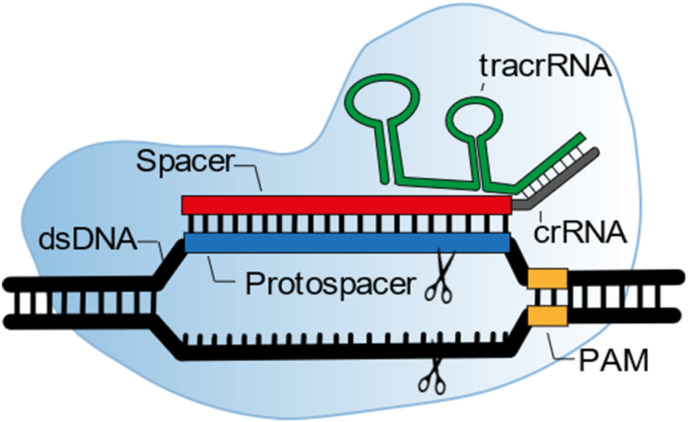
Fig. 2.
Schematic of Cas9 effector protein (light blue) during the dsDNA recognition process (black). In the case of Cas9 effector proteins, two crRNAs are associated by nucleotide hybridization. The tracrRNA (green) is crucial in the association between crRNA and effector protein, creating a RNP complex. The other crRNA has the spacer sequence (red), which could complement with a target sequences' protospacer (blue). The RNP complex can only unwind dsDNA next to a so-called PAM sequence (yellow). Without PAM sequence recognition by the RNP, no complementation between spacer and target sequence is possible. (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)