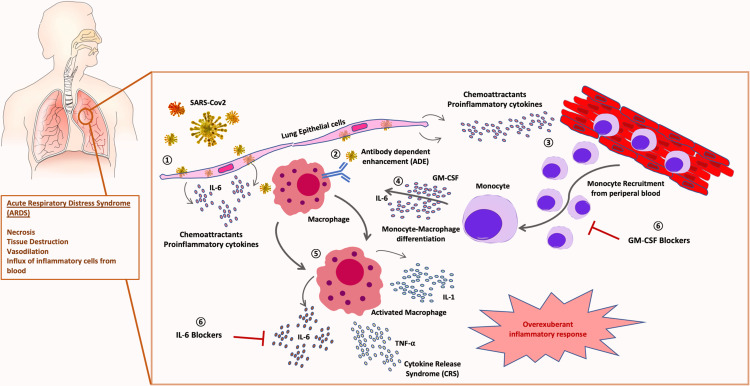
Figure 1.
Role of monocyte-macrophage in SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis: 1) SARS-CoV-2 infection of lung tissue induces release of chemoattractant proinflammatory cytokines by epithelial cells and fibroblasts. 2) Viral antibody-dependent enhancement (ADE) of macrophages could trigger SARS-CoV-2 infection of leucocytes. 3) Chemoattractant gradient induces massive recruitment of inflammatory monocytes from peripheral blood. 4) Monocyte-macrophage activation and differentiation is triggered by GM-CSF and IL-6. 5) An overexuberant activation of macrophages produces the cytokine release syndrome (CRS) responsible for the acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) typical of severe patients. 6) Therapeutical blockade of IL-6 and GM-CSF combination could avoid severe lung immunopathology in COVID-19 patients.