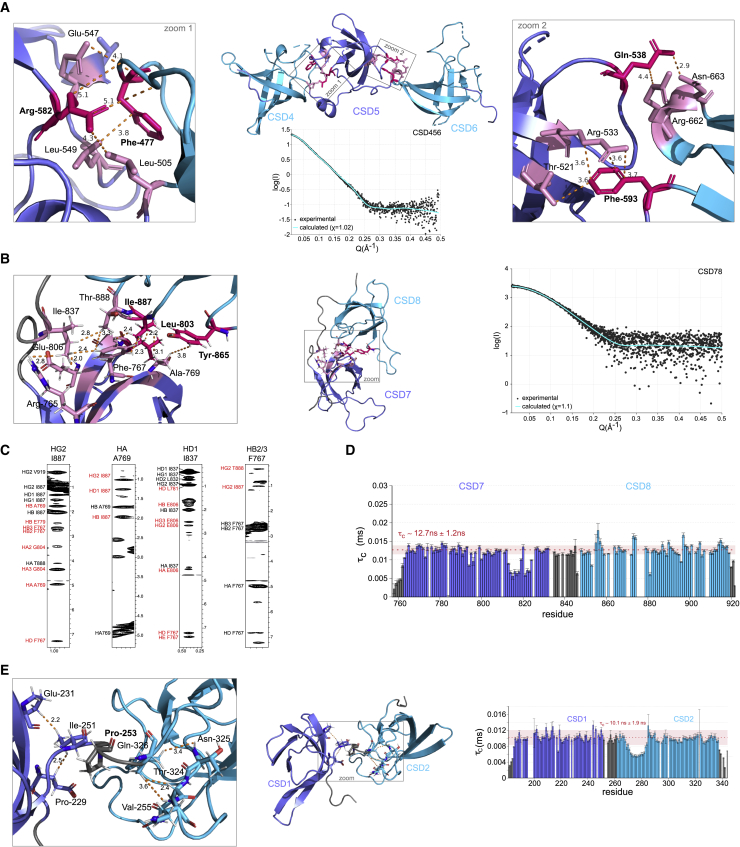
Figure 3.
Interdomain Contacts between Canonical CSDs and ncCSDs within Unr
(A) Interdomain contacts between CSD4 and CSD5 and between CSD5 and CSD6 derived from the crystal structure are highlighted in pink (boldfaced labeled residues colored in hot pink are mutated in experiments described below). The SAXS scattering curve of dCSD456 in solution (black dots) fits the back-calculated scattering density of the crystal structure (cyan) (χ = 1.02; SASBDB: SASDHJ7).
(B) The NMR solution structure of CSD78 shows a network of NOEs between both domains. These mostly hydrophobic interactions keep the domain arrangement fixed (highlighted in pink; residues labeled boldfaced and colored in hot pink are mutated in experiments described below). The SAXS scattering curve of dCSD78 in solution (black dots) fits to the back-calculated scattering density of the NMR structure (cyan) (χ = 1.1; SASBDB: SASDHK7).
(C) Exemplary NOE strips of the 3D 13C,1H,1H HMQC-NOESY spectrum of CSD78 highlight interdomain NOEs (red) that were detected and used in structure calculations.
(D) 15N relaxation data of CSD78 indicating joint tumbling of CSD7 and CSD8 in solution, with flexible regions (residues between R813 and L824) within the domains (flexible loop between β strands 4 and 5 of CSD7).
(E) CSD12 is lacking interdomain NOEs but shows only a three-residue-long linker, without NOEs, including one proline (labeled bold). Relaxation data of CSD12, indicating tumbling of the two single domains together in solution. Flexible residues are located between L270 and T285, which corresponds to an interdomain loop between β strand 1 and 2 in CSD2. The rotational correlation time (τc) derived from 15N longitudinal and transverse relaxation experiments is plotted per residue. The error bars indicate the error propagation from errors of the two relaxation experiments, which are derived from the quality of the exponential fit and the deviation between duplicates of two different relaxation delays.