Figure 5.
Influence of Unr Interdomain Contacts on Cofactor Binding
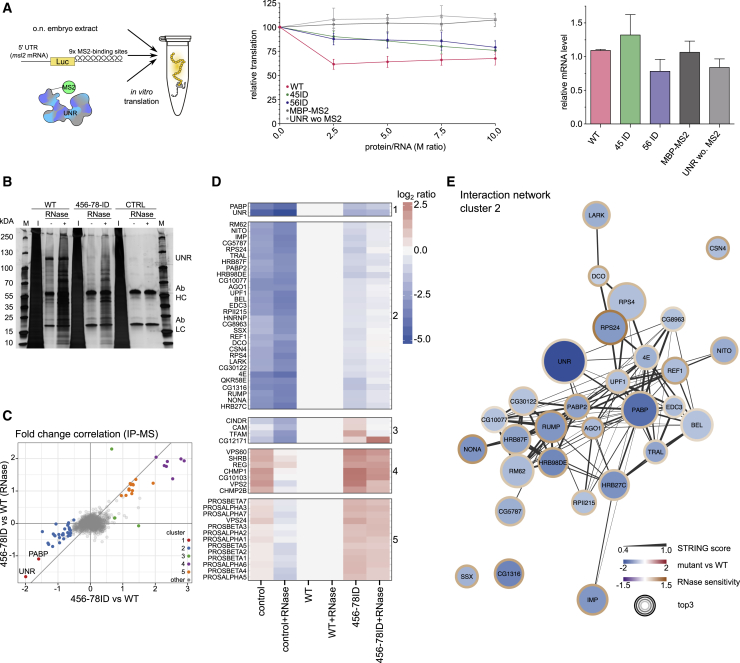
(A) Schematic representation of the in vitro translation assay. MS2-tagged Unr gets tethered to the 3′ UTR, which contains nine MS2 binding loops. Binding leads to repression of translation. The same mRNA construct was used before (Abaza and Gebauer, 2008) (BmutLMS2). Middle: relative in vitro translation of the firefly reporter gene over the internal control Renilla after adding increasing amounts of Unr; n = 3. Right: relative reporter mRNA levels after in vitro translation (point of 2.5 molar excess of Unr over RNA), measured by qRT-PCR; n = 3. The mean is shown for each data point, and the error bars indicate the standard deviation.
(B) A silver-stained polyacrylamide gel, showing the input (I) and elution samples with (+) and without (−) RNase treatment for WT, 456-78 ID, and the empty vector control that were used for the proteomics analysis. Unr, the antibody heavy chain (Ab HC), and the antibody light chain (ab LC) are labeled at the side of the gel.
(C) Scatterplot showing the correlation of interdomain mutant versus WT (x axis) and RNase-treated interdomain mutant versus RNase-treated WT (y axis). Colors indicate the cluster number from (D); n = 3.
(D) Heatmap representation of the different protein targets of WT and mutant protein samples. Proteins were clustered in five clusters using k means algorithm. The RNase-treated samples were normalized to the RNase-treated WT sample, and the non-treated samples were normalized to the non-treated WT sample. Red indicates upregulation and blue downregulation; n = 3.
(E) STRING interaction network, showing possible interactions between the targets that were enriched for the WT samples shown in clusters 1 and 2 of (D). The line thickness represents the STRING score, which represents the strength of data support for the individual interactions (Szklarczyk et al., 2019). The inner color of each circle represents the fold-change between interdomain mutant and WT sample; the border line color indicates the difference of enrichments of interdomain mutant versus WT between RNase-treated and non-treated (RNase sensitivity), and the size indicates the average abundance of a protein in the immunoprecipitation mass spectrometry run (top3 value), which correlates with the pull-down efficiency.