Figure 1.
Molecular Genetics of KCNG4 SNP rs140124801 and Analysis of KV2.1 Inactivation Properties
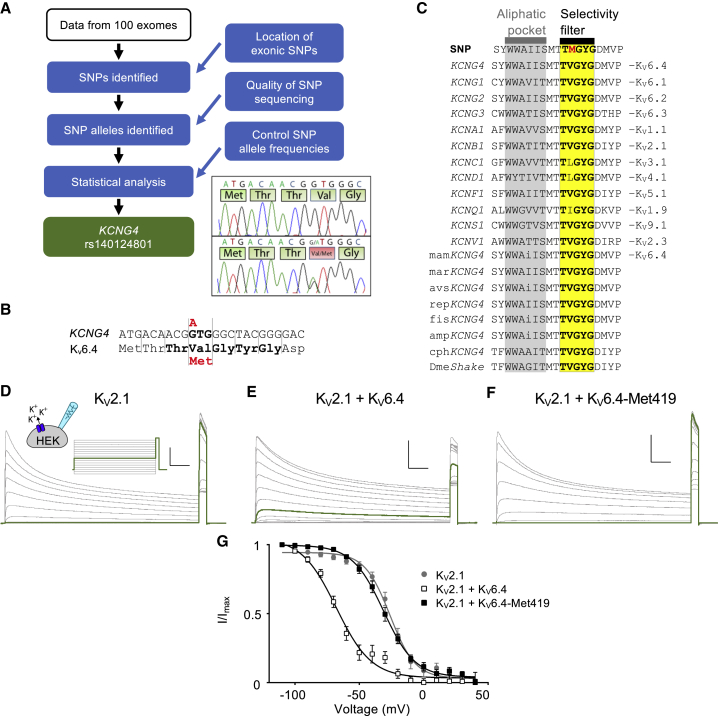
(A) Summary of the genetic analysis. The resultant finding is of the SNP rs140124801 in KCNG4. Inset: electrophoretograms showing the alleles.
(B) The nucleotide sequence of the SNP rs140124801 (NM_1.NM_172347.2), showing the altered GTG codon (boldface) and the rare allele (red). Amino acids 416–423 of KV6.4 (NP_758857.1) are shown below their nucleotide codons. The selectivity filter is shown in boldface, and the wild-type Val-419 is shown above Met-419.
(C) Evolutionary conservation of human KV6.4 positions 408–426: rs140124801 alleles and representative proteins of each human KV class and of KV6.4 in vertebrates. Invariant amino acids are capitalized. The selectivity filter TVGYG is shown in yellow and the conserved aliphatic region in gray.
(D–F) Representative current recordings to determine KV2.1 (D), KV2.1/KV6.4 (E), and KV2.1/KV6.4-Met419 (F) steady-state inactivation properties. The applied voltage protocol is illustrated above (D). Vertical scale bar, 10 nA; horizontal scale bar, 0.5 s. Green traces indicate currents recorded during the −40 mV conditioning step.
(G) Voltage dependence of steady-state inactivation of KV2.1 (gray filled circles, n = 9), KV2.1/KV6.4 (white squares, n = 12), and KV2.1/KV6.4-Met419 (black squares, n = 15). Symbols represent mean values, and error bars indicate SEM. Solid lines represent the Boltzmann fitted curves.