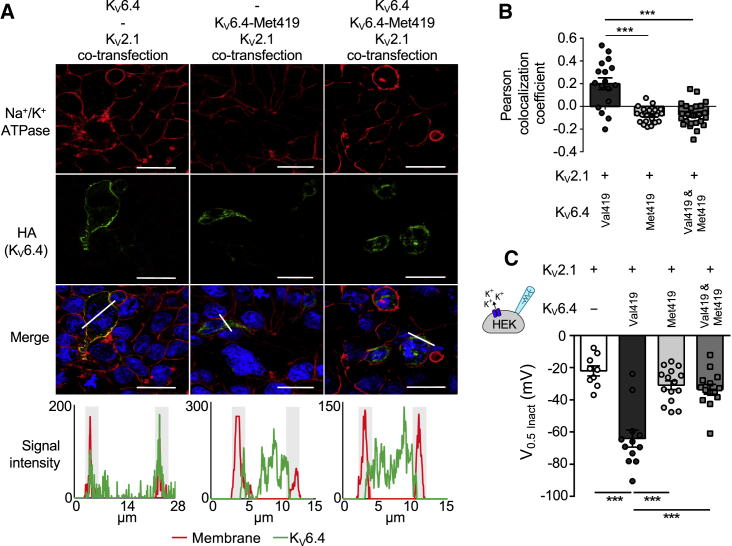
Figure 4.
Sub-cellular Localization and Electrophysiology Analysis of the Dominant-Negative Effect of Human KV6.4-Met419
(A) HEK293 and HeLa cells (separate experiments) were transfected with KV2.1 and wild-type KV6.4, KV6.4-Met419, or equimolar concentrations of KV6.4/KV6.4-Met419. Cell membranes were stained with Na+/K+ ATPase (red channel) and HA-tagged KV6.4 (green channel). HA-tagged KV6.4 localized to the cell membrane, showing significant co-localization with Na+/K+ ATPase. KV6.4-Met419 and KV6.4/KV6.4-Met419 co-expression showed cytoplasmic retention of KV6.4 and no evidence of co-localization with Na+/K+ ATPase. The graphs display the profiles of signals for the membrane and KV6.4.HA along the plane of the white line in the merged image. Note that the red and green signal co-localize in the KV6.4 experiment and are distinct in the KV6.4-Met419 and heterozygote experiment. Scale bars indicate 20 μm.
(B) Quantification of Pearson’s co-localization co-efficient between KV6.4.HA and Na+/K+ ATPase under each experimental condition. For each condition, at least 17 cells were counted from three independent experiments.
(C) V0.5 act from inactivation protocols shown in Figures 1D–1G. Co-expression of KV6.4 and KV6.4-Met419 with KV2.1 failed to evoke a shift in the voltage dependence of inactivation.
Bars indicate mean values, error bars indicate SEM, n = 9–15, ∗∗∗p < 0.001. The statistics in (B) and (C) represent one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test.