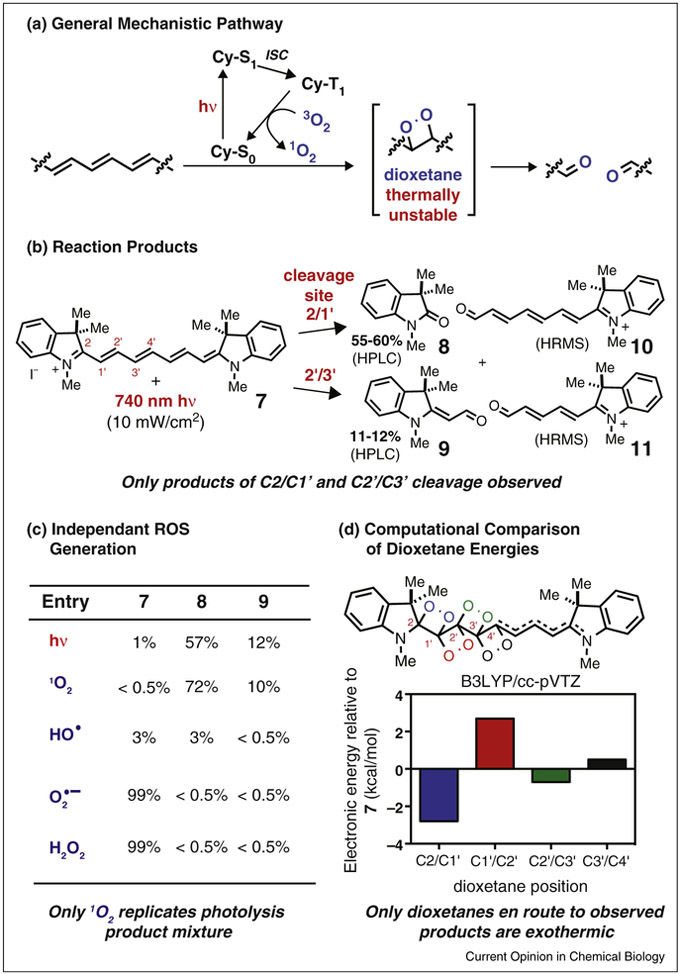
Figure 2.
Probing the mechanism of cyanine photooxidation. (a) General reaction pathway. (b) Carbonyl products 8-11 resulting from regioselective formation and then cleavage of dioxetanes at the C2/C1′ and C2′/C3′ positions on the polyene. (c) Relative product mixture resulting from exposure of 7 to either 740 nm light or candidate ROS. Only 1O2 produces product ratios similar to those obtained with direct photolysis. (d) Energies of possible dioxetane intermediates en route to carbonyl products.