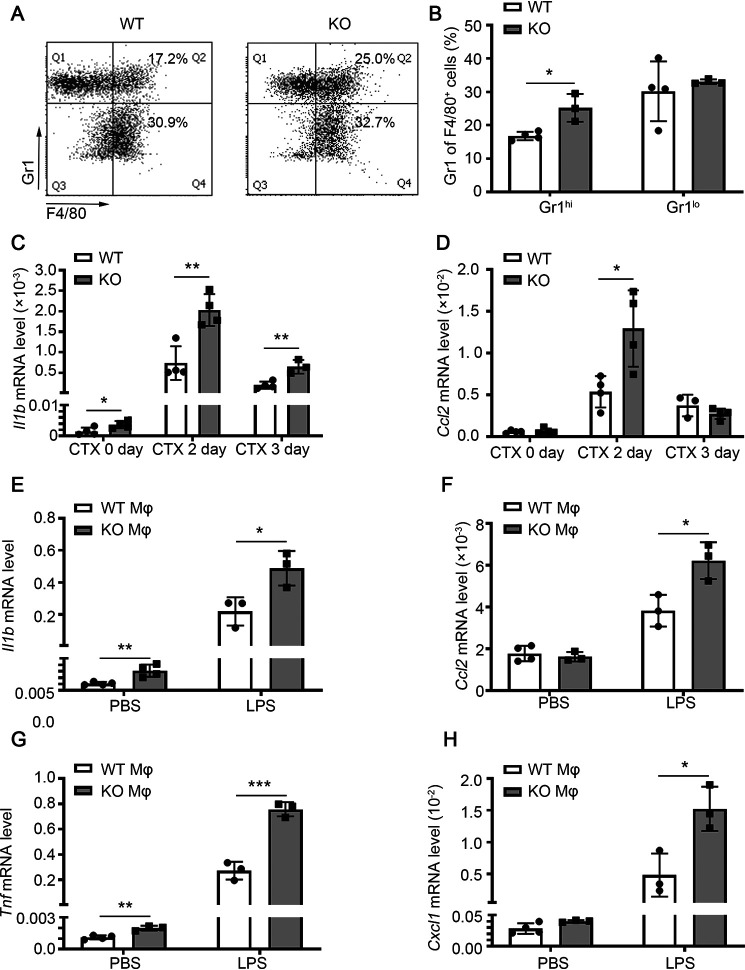
Figure 6.
miR-223-3p KO increases proinflammatory macrophage infiltration of injured skeletal muscle. A, representative flow cytometry analysis of CD45+ CD11b+ F4/80+ Gr1hi proinflammatory macrophages and CD45+ CD11b+ F4/80+ Gr1lo anti-inflammatory macrophages in the muscle total macrophages of WT and miR-223-3p KO mice 1 day after CTX injury. B, percentages of CD45+ CD11b+ F4/80+ Gr1hi macrophages and CD45+ CD11b+ F4/80+ Gr1lo anti-inflammatory macrophages in the muscle total macrophages of WT and miR-223-3p KO mice at 1 day after CTX injury (n = 3–4 per group). C–D, RT-PCR assessment of Il1b and Ccl2 expression in the muscles of WT and miR-223-3p KO mice at 0, 2, and 3 days after CTX injury (n = 3–4 per group). E–H, RT-PCR assessment of Il1b, Ccl2, Tnf, and Cxcl1 expression in WT and miR-223-3p KO primary macrophages (mφ) treated with PBS or LPS (5 μg/ml) for 12 h (n = 3–4 per group). Data are expressed as the mean ± S.D. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001 by unpaired two-tailed Student's t test.