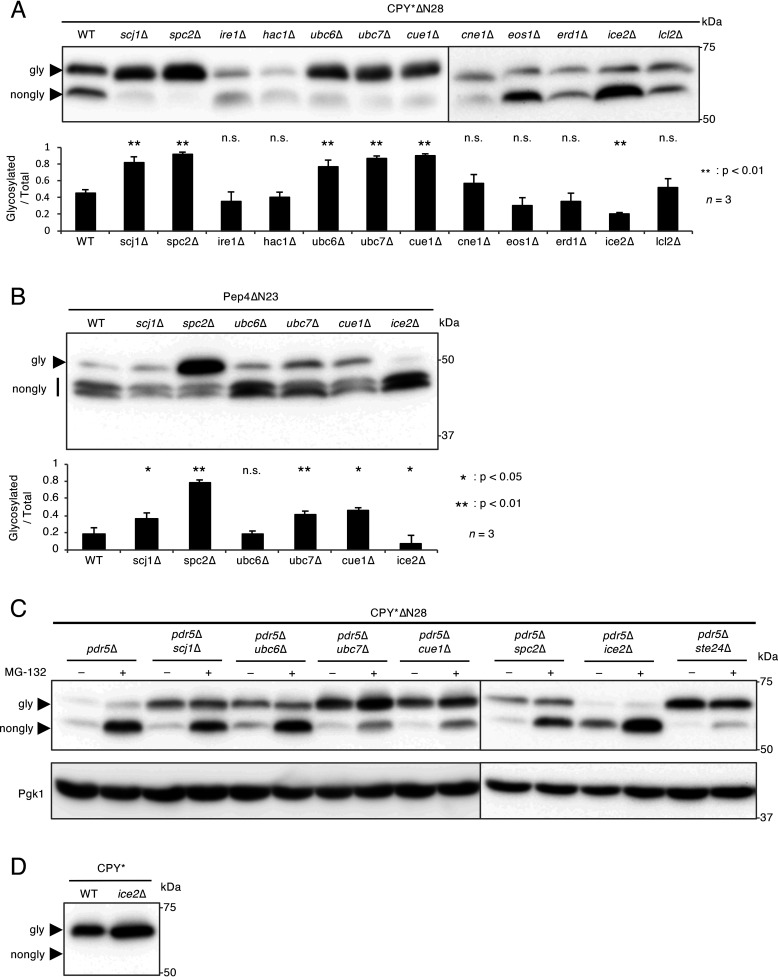
Figure 3.
Spc2 is involved in the suppression of N-terminal signal peptide-independent protein translocation. A, Western blot analysis of CPY*ΔN28 expressed in mutants defective in ER functions. CPY*ΔN28-V5 was expressed and analyzed as described in the legend to Fig. 1. The bar graph shows the relative ratio of glycosylated versus total CPY*ΔN28 proteins. n represents the number of biological replicates. B, Western blot analysis of Pep4ΔN23 expressed in the scj1Δ, spc2Δ, ubc6Δ, ubc7Δ, cue1Δ, and ice2Δ mutants. Pep4ΔN23 tagged N terminally with the DYKDDDDK epitope was expressed and analyzed as described above. The ratio of glycosylated versus total Pep4ΔN23 proteins was represented as a bar graph. n represents the number of biological replicates. C, accumulation of nonglycosylated CPY*ΔN28 expressed in the pdr5Δ scj1Δ, pdr5Δ ubc6Δ, pdr5Δ ubc7Δ, pdr5Δ cue1Δ, pdr5Δ spc2Δ, pdr5Δ ice2Δ, and pdr5Δ ste24Δ mutants treated with MG-132. CPY*ΔN28-V5 was expressed in the indicated cells. Cells were treated with 50 μm MG-132 for 1 h before protein extraction. Samples were subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by immunoblotting using an anti-V5 antibody. The immunoblot was also probed with an anti-Pgk1 antibody as a loading control. D, Western blot analysis of CPY* expressed in the ice2Δ mutant. CPY*-V5 was expressed and analyzed as described above.