Figure 4.
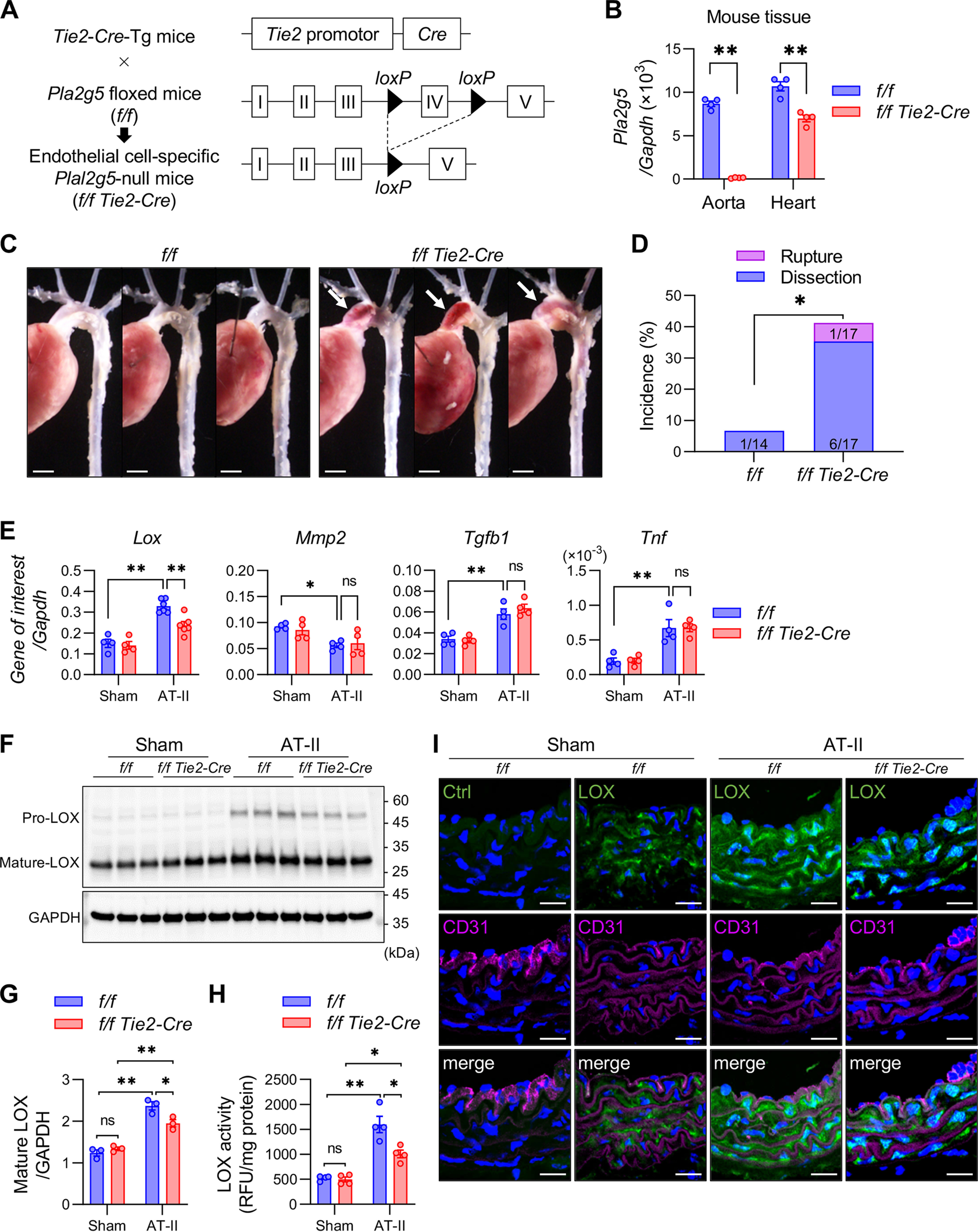
Increased aortic dissection in EC-specific Pla2g5-null mice. A, schematic procedure for generation of EC-specific Pla2g5-null mice. B, expression of Pla2g5 mRNA relative to Gapdh in the aorta and heart of control (f/f) and EC-specific Pla2g5-null (f/f Tie2-Cre) mice (n = 4). C, representative thoracic aortas of control and EC-specific Pla2g5-null mice after 7 days of AT-II infusion. Arrows indicate aortic dissection with intramural hematoma. Scale bars, 1 mm. D, incidence of thoracic aortic dissection or rupture in control (n = 14) and EC-specific Pla2g5-null (n = 17) mice within 7 days of AT-II infusion. E, mRNA expression of Lox, vascular remodeling markers (Mmp2, Acta2, and Tgfb1), and pro-inflammatory cytokine (Tnf) in the aortas of control and EC-specific Pla2g5-null mice with or without AT-II infusion for 48 h (n = 4–6). Shown are immunoblot analysis of LOX protein, with GAPDH as an internal control (F), densitometric analysis of mature LOX protein relative to GAPDH (n = 3) (G), and LOX activity (n = 4) (H) in the aortas of control and EC-specific Pla2g5-null mice with or without AT-II infusion for 48 h. I, immunofluorescence of aortas of control and EC-specific Pla2g5-null mice with or without AT-II infusion for 48 h using control IgG (Ctrl) or anti-LOX antibody (green) and anti-CD31 antibody (magenta) with DAPI (blue). Scale bars, 20 μm. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ns, not significant by two-way ANOVA (B, E, G, and H) and by Fisher's exact test (D). Data are presented as mean ± S.E. (error bars) of the indicated number (n) of biological replicates.
