Figure 2.
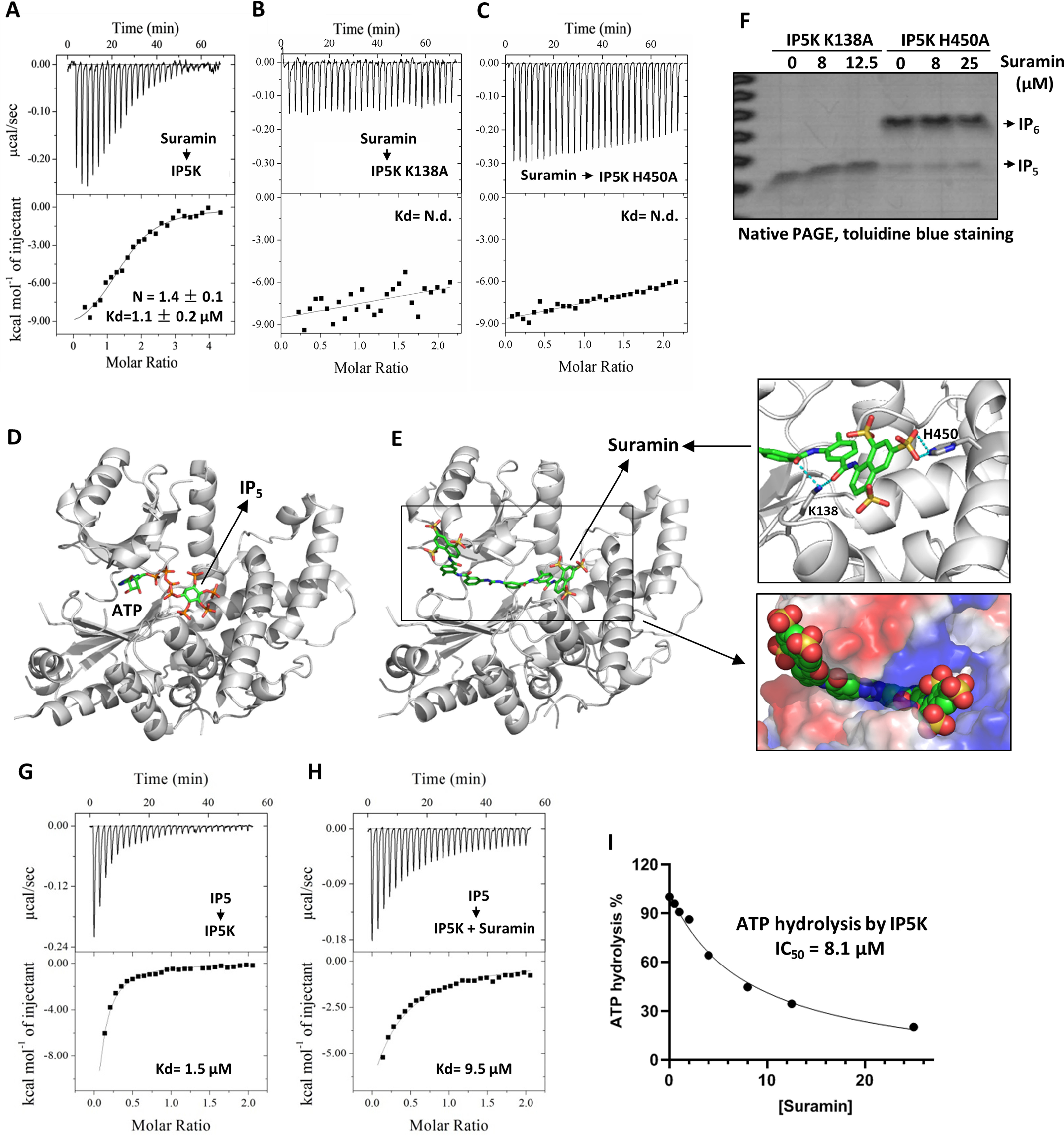
Mechanistic basis of IP5K inhibition by suramin. A–C, quantitative ITC measurement of suramin binding to IP5K WT (A), K138A (B), and H450A (C) mutant proteins. D, the ATP and IP5 binding sites in the crystal structure of IP5K (PDB code 5MW1). E, docking generated structural model of the suramin–IP5K complex with the lowest free energy value. Right top panel, close-up view of the docked model. Potential suramin-interacting residues (Lys138 and His450) are shown as sticks. Right bottom panel, close-up view of the docked model with IP5K shown in surface and suramin shown as spheres. F, catalytic activity of IP5K-K138A and IP5K-H450A in the presence/absence of suramin, measured by the native PAGE assay. G and H, quantitative ITC measurement of IP5–IP5K binding affinity in the absence (G) and presence (H) of suramin (20 μm). I, suramin dose-dependently inhibits the IP5-independent ATP hydrolysis activity of IP5K, measured by the ADP-GloTM kinase assay. N.d., not detected.
