Figure 3.
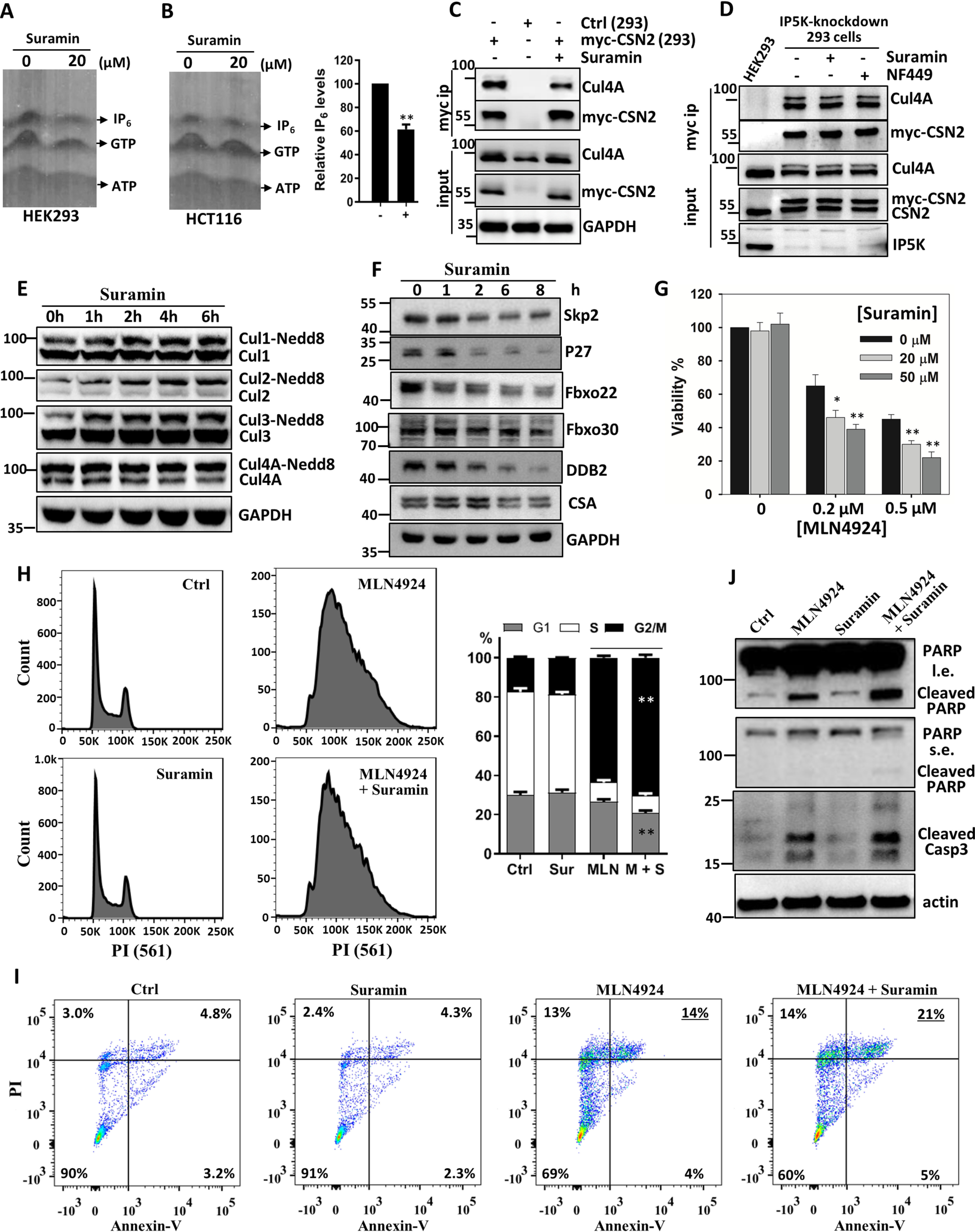
Suramin inhibits IP5K function in vivo. A and B, effect of suramin (20 μm, 12 h) on cellular IP6 levels in HEK293 (A) and HCT116 (B) cells. IP6 was extracted from cells for PAGE separation and toluidine blue staining. B, right panel, bar graph quantification of relative IP6 levels in HCT116 cells after normalization to cell number. C, immunoprecipitation of myc-CSN2 from myc-CSN2-HEK293 stable cell line treated with or without suramin for 8 h. D, immunoprecipitation of myc-CSN2 from myc–CSN2–HEK293 stable cell after IP5K knockdown, with or without suramin or NF449 treatment. E, Western blotting analysis of Cullin neddylation levels in HCT116 cells after treatment with 20 μm suramin for the indicated time periods. F, Western blotting analysis of the CRL substrate receptors and ubiquitylation substrate p27 after treatment with suramin (20 μm) for the indicated time periods. G, effect of MLN4924, alone or in combination with suramin, on cell viability. HCT116 cells were treated with MLN4924, suramin, or both for 48 h to examine cell viability. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01 (Student's t test). H, HCT116 cells were treated with MLN4924 (0.5 μm), suramin (20 μm), or both for 24 h. DNA profiles of treated cells were analyzed by flow cytometry after PI staining. Right panel, bar graph representation of the cell cycle data expressed as means ± standard deviation. **, p < 0.01 (Student's t test). I, HCT116 cells were treated as described for H and then stained with FITC-conjugated annexin V and PI before being analyzed by flow cytometry. J, HeLa cells were treated as described in H. After 40 h, apoptosis marker proteins were blotted. Ctrl, control; Sur, suramin; MLN, MLN4924; M + S, MLN4924 and suramin.
