Figure 2.
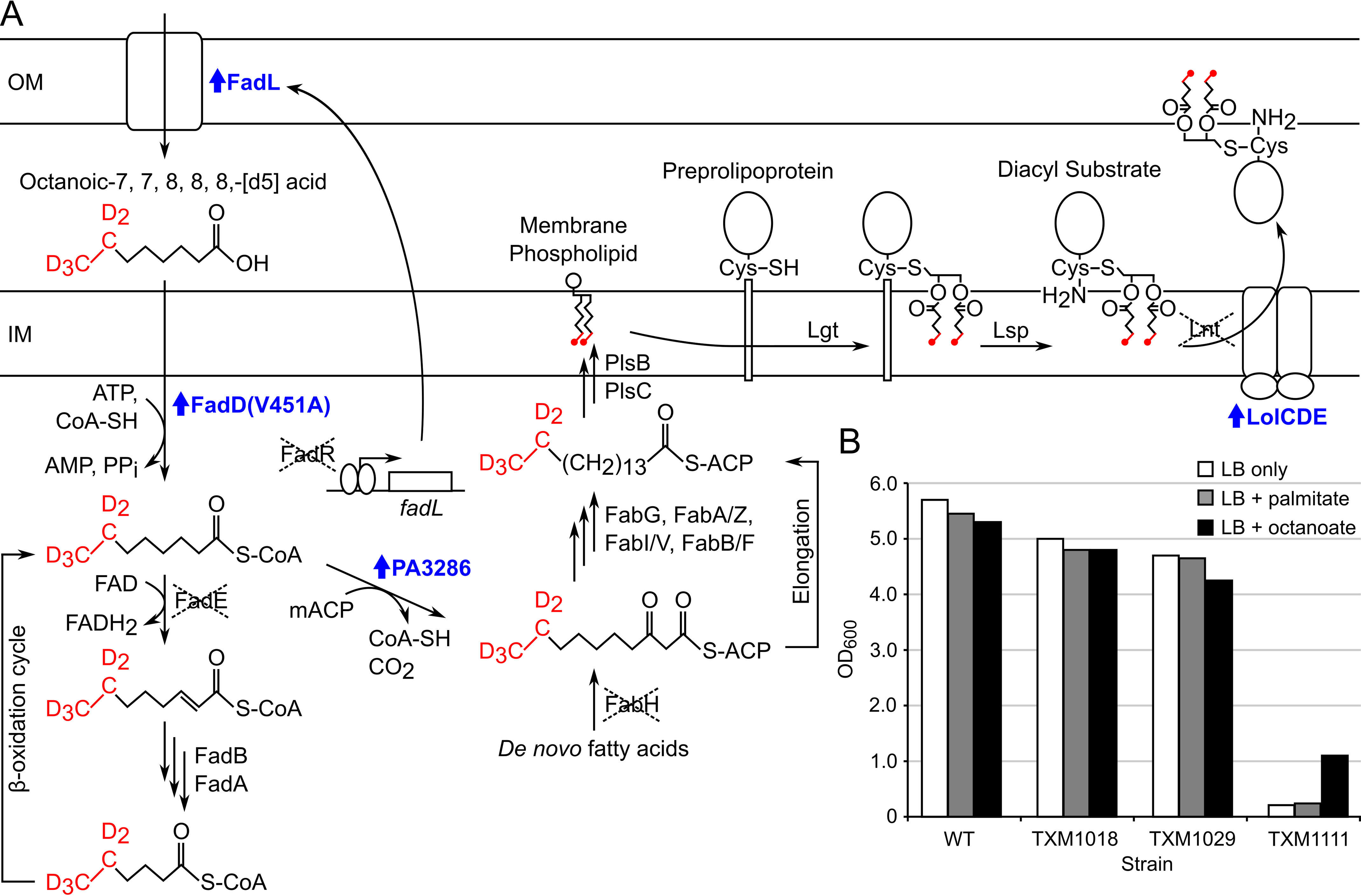
Production of acyl-labeled [d5]-DA-LP in strain TXM1111. A, exogenous octanoic-7,7,8,8,8-[d5] acid (labeled in red) is transported across the OM by constitutively expressed FadL upon deletion of FadR. Activation by esterification with CoA is enhanced by introduction of the FadD(V451A) allele. Entry of [d5]-octanoate substrate into the E. coli β-oxidation pathway is prevented by the deletion of FadE so that plasmid-encoded P. aeruginosa protein PA3286 can shunt the acyl-CoA ester intermediate into the FAS pathway by condensation with malonyl-ACP (mACP). Deletion of FabH precludes incorporation of unlabeled de novo fatty acids. Following cycles of elongation by FAS, [d5]-labeled acyl chains are incorporated into membrane phospholipids by PlsB and PlsC. Lipoprotein biosynthesis proceeds as normal, with the deuterium-labeled DA moiety transferred by Lgt from a phospholipid donor to the cysteine thiol of the preprolipoprotein. Lsp cleaves the signal peptide of the lipoprotein, exposing the α-amino group of the lipidated cysteine, to yield labeled [d5]-DA-LP. Overexpression of the ABC transporter LolCDE helps export the nonoptimal [d5]-DA-LP substrate to the OM and allows Lnt to be deleted. Up-regulated genes are labeled in blue. B, BW25113 WT (WT) and derivatives TXM1018 (fadR::Tmpr, lpp::FRT, fadE::Tetr), TXM1029 (fadR::Tmpr, lpp::FRT, fadE::Tetr + PA3286 + lolCDE), and TXM1111 (fadR::Tmpr, lpp::FRT, fadE::Tetr, fabH::FRT, lnt::Sptr + PA3286 + lolCDE + fadD(V451A)) were grown in LB only, or LB supplemented with 100 μg/ml of palmitate or octanoate. The final culture density (OD600) was measured after 19 h.
