Figure 2.
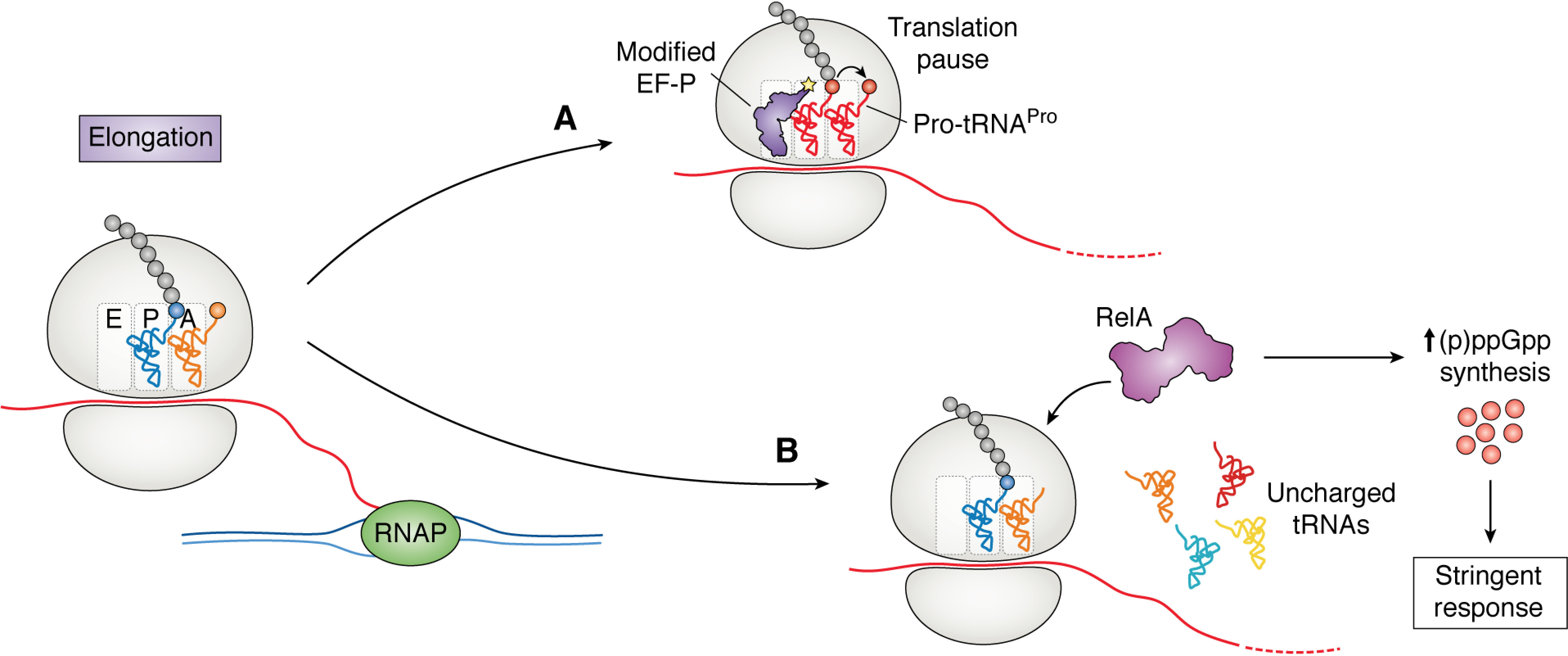
Regulation of gene expression at the level of translation elongation. A, translation pausing can be induced by the slow peptide bond formation between proline residues (red). These pauses are relieved by the translational elongation factor EF-P, which facilitates proline–proline bond formation. B, when uncharged tRNA enters the A-site of the ribosome under starvation conditions, it is recognized by RelA. RelA synthesizes (p)ppGpp, inducing the stringent response. The stringent response stimulates widespread regulatory functions in the cell, including regulation translation through the control of ribosome biosynthesis.
