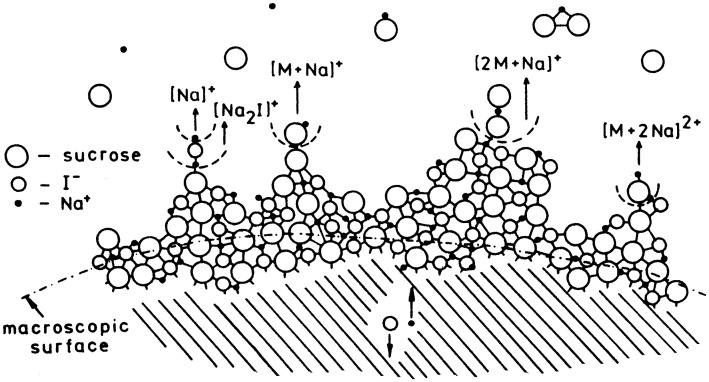
Figure 14.
Representation of the extraction and desolvation mechanism for various ions from a nearly solid or glassy state of a mixture of sucrose and NaI. On a molecular scale, the surface is rough, almost free of solvent, and of low ionic conductivity. Due to some mobility in the layer, charge separation leads to protuberances, desolvation of ionic species, and finally their release into the gas phase. A continuous reconstruction of the surface provide continuous supply. Reproduced from Ref. [106] by kind permission. © Elsevier Science Publishers, 1984.