Fig. 6.
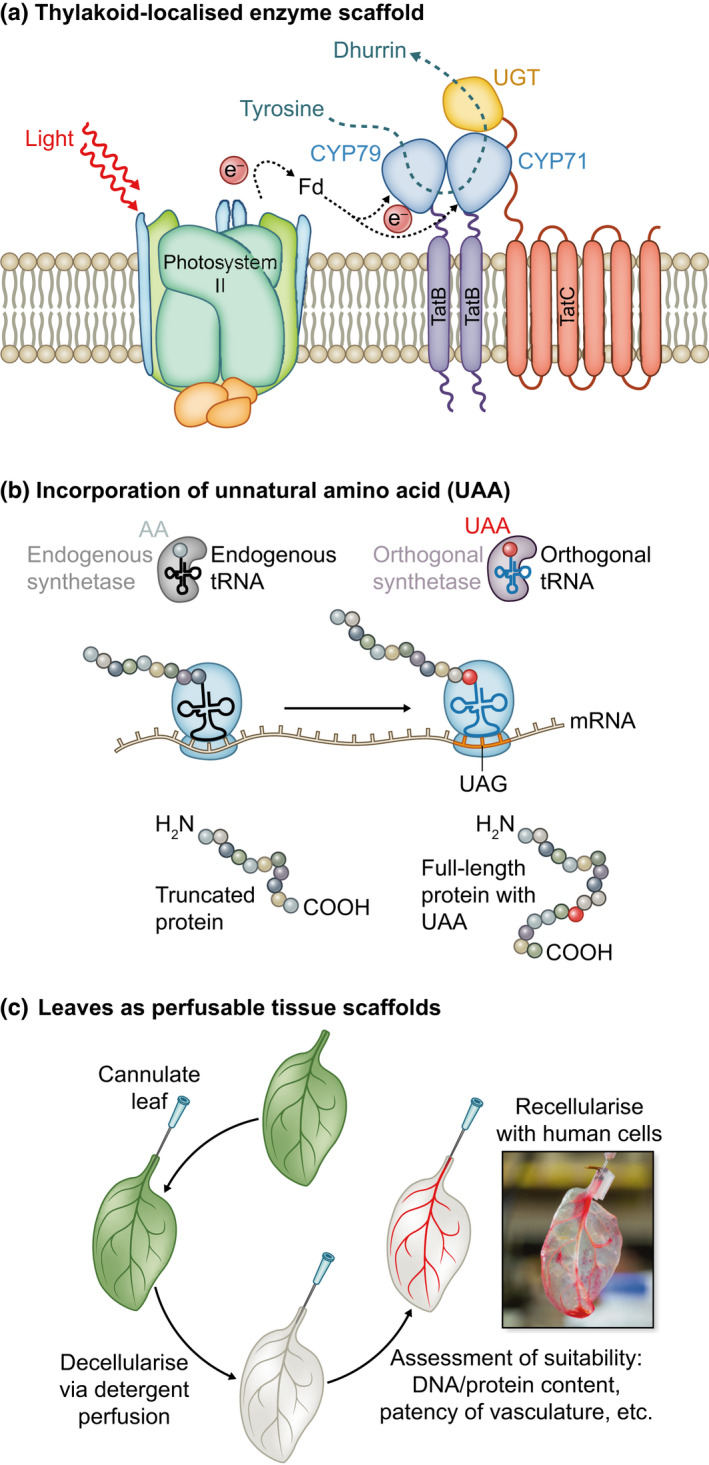
Prototypes of emerging areas in plant synthetic biology. (a) Scaffolding of a UDP glucosyl transferase and two cytochrome P450s (CYP97 and CYP 71) in the thylakoid membrane by fusion to ΔpH‐dependent twin‐arginine translocation (TatB and TatC) transmembrane proteins. Ferredoxin (fd) serves as an electron donor. Adapted from Henriques de Jesus et al. (2017). (b) Unnatural amino acids (UAA) are incorporated into heterologous proteins by expression of orthologous tRNA and tRNA‐synthetase pairs. In the system deployed in Arabidopsis, these recognise the rare UAG amber stop codon. When the UAA is supplied it is incorporated into the polypeptide chain resulting in the production of a full‐length protein. Adapted from Li et al. (2013). (c) Leaves used in engineering human tissues are decellularised with detergents. The vascular system is then recellularised with specific human cell types. These can be supplied with nutrients through the vascular system, enabling them to form tissues with novel structures. Adapted from Gershlak et al. (2017).
