Figure 1.
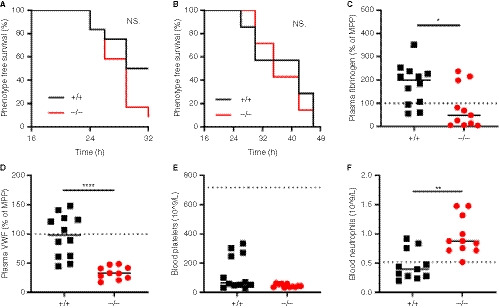
Hypercoagulability mediated venous thrombosis through siRNAs targeting Serpinc1 and Proc in SLC44A2 deficient mice. A, Phenotype free survival in SLC44A2 deficient mice (Slc44a2− / −, −/−) and littermate wild type controls (Slc44a2+ / +, +/+) shown as percentage following injection with 80nmol/kg siRNA (n = 12 per group). B, Phenotype free survival following injection with 60nmol/kg siRNA (n = 6 per group). The following blood parameters were measured after treatment with 80nmol/kg siRNA: (C) Plasma fibrinogen levels 32 hours post‐treatment expressed as a percentage of MPP (mouse pool plasma), (D) plasma VWF (von Willebrand factor) levels 32 hours post‐treatment expressed as a percentage of MPP (mouse pool plasma), (E) blood platelet counts at time of sacrifice. For reference platelet levels of Slc44a2+ / + before siRNA treatment are represented by the dotted line (mean cell counts). F, Circulating neutrophil levels at time of sacrifice. For reference platelet levels of Slc44a2+ / + mice before siRNA treatment are represented by the dotted line (mean cell counts). Statistical analysis for phenotype free survival determined using Mantel‐Cox test. Solid line represents median value. Statistical differences were evaluated using Mann‐Whitney rank‐sum test (NS = non‐significant; *signifies P < .05; **signifies P < .01; ****signifies P < .0001)
