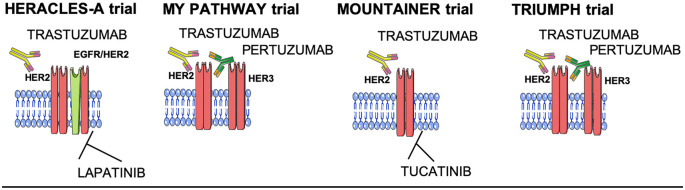
Figure 2.
Recent anti-HER2 strategies in mCRC. MET tyrosine kinase receptor activation and overexpression have been investigated as a potential mechanism of both primary and acquired resistance to anti-EGFR treatment and BRAF inhibitor combinations in BRAFV600E mutant CRC.39 Data from in vitro and in vivo studies have shown that CRC xenograft models with MET amplification do not respond to anti-EGFR antibodies.40 MET amplifications have been found in only a small percentage (1–2%) of the CRC population upfront, but a study found that using NGS liquid biopsies in an anti-EGFR refractory setting the prevalence of MET amplification could rise to 20%.41 Preliminary studies with MET inhibitors such as SYM015 suggest the resistance could be overcome, with a clear implication for ongoing clinical trials currently exploring these agents.42
CRC, colorectal cancer; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; mCRC, metastatic colorectal cancer; NGS, next-generation sequencing.