Fig. 1.
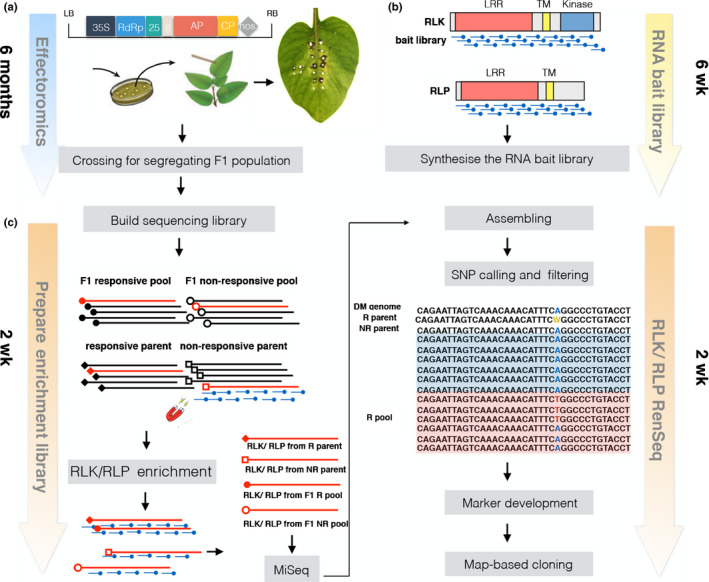
Overview of the effectoromics and receptor‐like protein/kinase enrichment sequencing (RLP/KSeq) pipeline for the fast identification and mapping of surface immune receptors. (a) Predicted Phytophthora infestans apoplastic effectors are cloned into the binary potato virus X (PVX) vector pGR106 and transformed into Agrobacterium tumefaciens for functional screening by PVX agroinfection. Agroinfected leaves are scored at 10–14 d post‐infection (dpi) for occurrence of cell death phenotypes. Responsive (R) and nonresponsive (NR) genotypes are crossed to create segregating F1 populations. (b) Prediction of the RLP and RLK genes from the reference genome enables the design and synthesis of the RLP/RLK bait library for bespoke target enrichment sequencing in the selected plant species. (c) An F1 population is screened for segregation of the recognition phenotype and pooled, based on their response pattern. Responsive and nonresponsive pools as well as the respective parents are subjected to enrichment sequencing. RLP/KSeq‐derived reads are mapped to the reference genome, and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) linked to the recognition phenotype identified. Candidate markers are tested on the segregating population by SNP genotyping technologies such as LightScanner.
