Fig. 3.
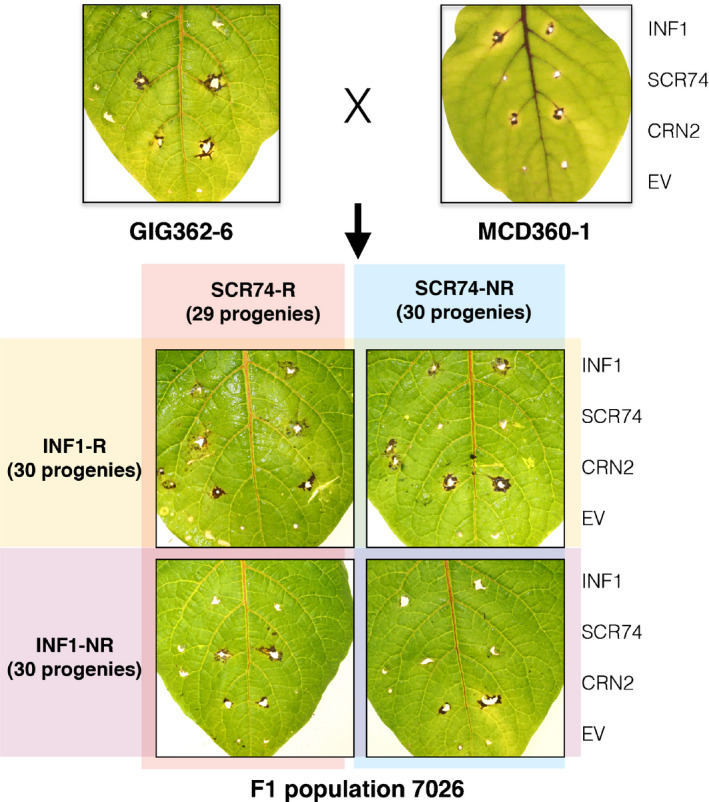
Independent segregation of responses to SCR74 and INF1 in F1 population 7026 of Solanum microdontum. Solanum microdontum ssp. gigantophyllum GIG362‐6 (SCR74 responsive) was crossed with S. microdontum MCD360‐1 (INF1 responsive) and progeny plants were assessed for phenotypic respsponses to INF1 and SCR74 through agroinfection with pGR106‐INF1 and pGR106‐SCR74. The empty vector pGR106 and the vector containing the CRN2 cell death‐inducer, pGR106‐CRN2, were included as negative and positive controls, respectively. For INF1, 30 responsive (INF1‐R) and 30 INF1 nonresponsive (INF1‐NR) progeny plants were identified. Similarly for SCR74, 29 and 30 SCR74 responsive (SCR74‐R) and SCR74 nonresponsive (SCR74‐NR) progeny plants were selected for the receptor‐like protein/kinase enrichment sequencing (RLP/KSeq) , respectively. Representative images are shown at 14 d post‐infection (dpi).
