Fig. 4.
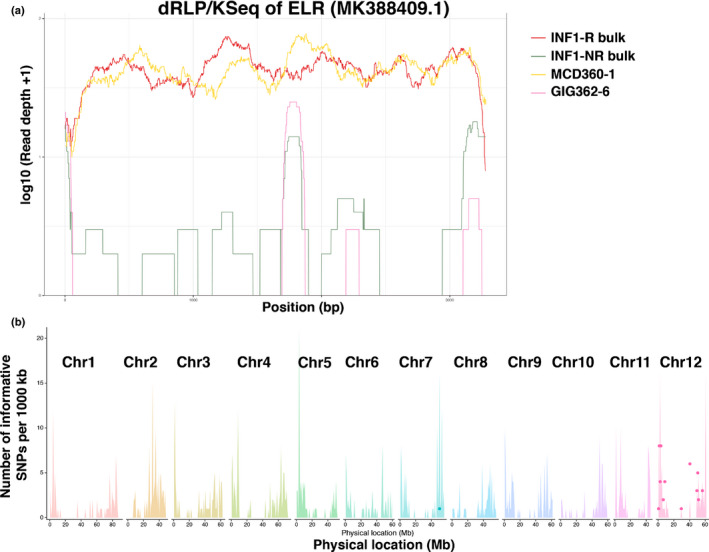
ELR was recovered and independently mapped to chromosome 12 by receptor‐like protein/kinase enrichment sequencing (RLP/KSeq). (a) Diagnostic RLP/KSeq for ELR. The x‐axis depicts the coding DNA sequence (CDS) of ELR from start to stop and the y‐axis indicates the read coverage of functional ELR with RLP/Kseq‐derived reads mapped to the reference under highly stringent conditions on a log scale. The yellow and red horizontal lines indicate full‐length ELR sequence from Solanum microdontum MCD360‐1 and INF1 responsive bulk without any sequence polymorphisms, respectively. The green and pink lines show a low and discontinuous read‐coverage from S. microdontum ssp. gigantophyllum GIG362‐6 and INF1 nonresponsive bulk, respectively. (b) Mapping of ELR. The x‐axis represent the physical positions of the 12 individual potato chromosomes and the y‐axis the number of RLP/receptor‐like kinases (RLKs) or single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) per 1 Mb bin. The background colour spikes represent the number and position of annotated RLP/RLKs and the coloured dots depict the position of significant and linked SNPs in a 1 MB bin. The peak in chromosome 12 indicates various SNPs that are linked with ELR, which confers response to INF1.
