Fig. 6.
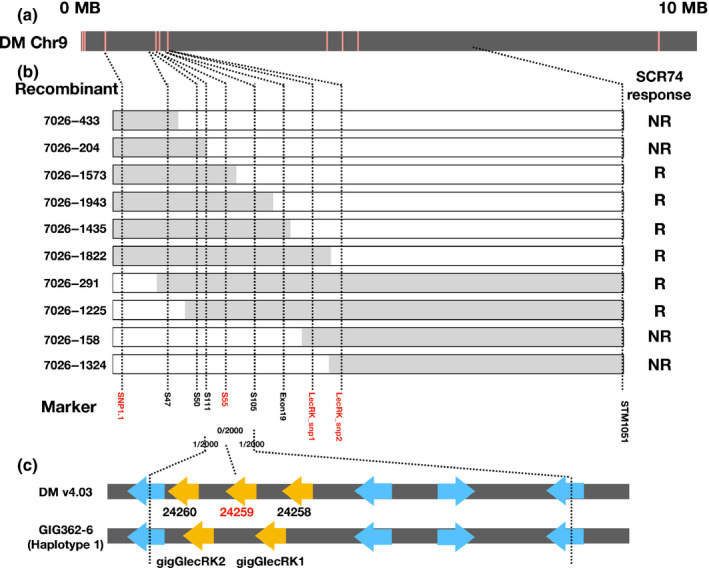
Fine‐mapping the SCR74 response gene to a G‐LecRK locus. (a) Graphical representation of the top 10 Mb of chromosome 9 of S. tuberosum Group Phureja DM1‐3 (DM) (black bar) and the location of informative single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) (red lines). (b) Overview of recombinant screening, showing representative recombinants with their genotyping and phenotyping results abbreviated as (R) for response and (NR) for nonresponse to SCR74. The position of the responsive haplotype of Solanum microdontum ssp. gigantophyllum GIG362‐6 (grey bar), the nonresponsive haplotype of S. microdontum MCD360‐1 (white bar) and the markers (dotted lines) are indicated. Receptor‐like protein/kinase enrichment sequencing (RLP/KSeq)‐derived markers are shown in red. (c) The G‐LecRK locus of DM1‐3 (v.4.03) and GIG362‐6 based on the sequencing of a bacterial artificial chromosome (BAC) clone that spans the SCR74‐responsive interval on chromosome 9. The locations of G‐LecRK (yellow arrows) and other predicted genes (blue arrows) are marked.
