Figure 2.
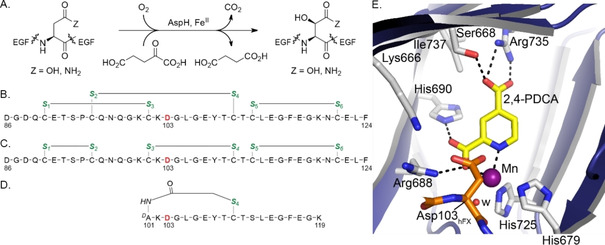
AspH catalyses the hydroxylation of the Asp/Asn‐residues of specific EGFD disulfide isomers. A) Scheme for the AspH‐catalysed hydroxylation of Asp/Asn‐residues in EGFDs. B) The canonical (Cys 1–3, 2–4, 5–6) EGFD1 disulfide pattern of human coagulation factor X (hFX amino acids 86–124); the AspH hydroxylation site (Asp103hFX) is in red, cystine thiols in green. C) The noncanonical (Cys 1–2, 3–4, 5–6) hFX EGFD1 disulfide isomer. D) A cyclic thioether peptide (hFX‐CP101‐119) mimicking the central noncanonical (Cys 3–4) hFX EGFD1 disulfide fold containing the AspH hydroxylation site Asp103hFX (red).23 E) Close‐up of the AspH active site in the AspH:2,4‐PDCA crystal structure (PDB ID: 5JTC).24 The key residues engaged in 2,4‐PDCA (Ser668, Arg688, His690, and Arg735) and metal binding (His679, His725) are shown. A pocket formed by AspH residues Ser668, Ile737, His690, Arg688, and Lys666 adjacent to the C‐3 position of 2,4‐PDCA is sufficiently large to accommodate substituents at the C‐3 position of 2,4‐PDCA. Colours: violet/grey: His6‐AspH315‐758; yellow: carbon‐backbone of 2,4‐PDCA; orange: carbon‐backbone of a synthetic hFX EGFD1‐derived peptide; purple: Mn; red: oxygen; blue: nitrogen. w: water.
